What Is OLA?
An OLA Is An Internal Agreement That A Service Provider Creates For Their Internal Teams So That They Do Not Breach The Slas. OLA Is Used To Trace Internal Service Commitments.
In simple words, an OLA informs internal teams about how much time they need to resolve the ticket. On top of that, it also informs what will be the consequences if the time limit has crossed.
In this technology-enabled marketplace, delivering outstanding IT services is essential. However, organizations must follow certain practices to maximize IT productivity while maintaining costs as low as possible. OLA (Operational Level Agreement) is one of the processes that service providers need to follow.
Why Is OLA Needed?
The OLAs are designed to align the actions or participation of several support teams to deliver the service to the end-user maintaining the intended SLA of the service provider. This is because the internal teams involved in delivering the service, might not necessarily be aware of the actual promised time of delivery by the service provider.
Such agreements are essential for internal teams that are involved in delivering the service, as they might not necessarily be aware of the actual SLA of the service provider.
Consequently, OLAs are used to streamline the workforce calculation among the groups that are involved, which will eventually help the internal services in making commitments and still provide the services within the suggested SLA to the customers.
Elements Of OLA
At the ground level, the OLA works as a document that operates as a matter of record between parties and includes the following elements:
General Overview
The two things included in the general overview are the objective among parties and the aim of the agreement.
Parties Responsible
All the stakeholders will be listed here in this section including their names, designations, and roles.
Roles and responsibilities of the service provider
This section is essential for knowing every external and internal service provider and their allocated roles and responsibilities in detail.
Hours of Coverage, Response Times, and Escalations
The operating hours, response times, and escalation policies can be mentioned in this section.
Reporting, Reviewing & Auditing
This section is for referring to the tenure of the OLA and defining a schedule or timeframe for internal audits, evaluations, and reporting.
OLA vs SLA – What’s the difference?
People often think that OLA is like an SLA, however, the content of an OLA still differs from an SLA. Check out the image below to see the differences.
The key differences between OLAs and SLAs are as follows:
How To Leverage OLA In ServiceOps?
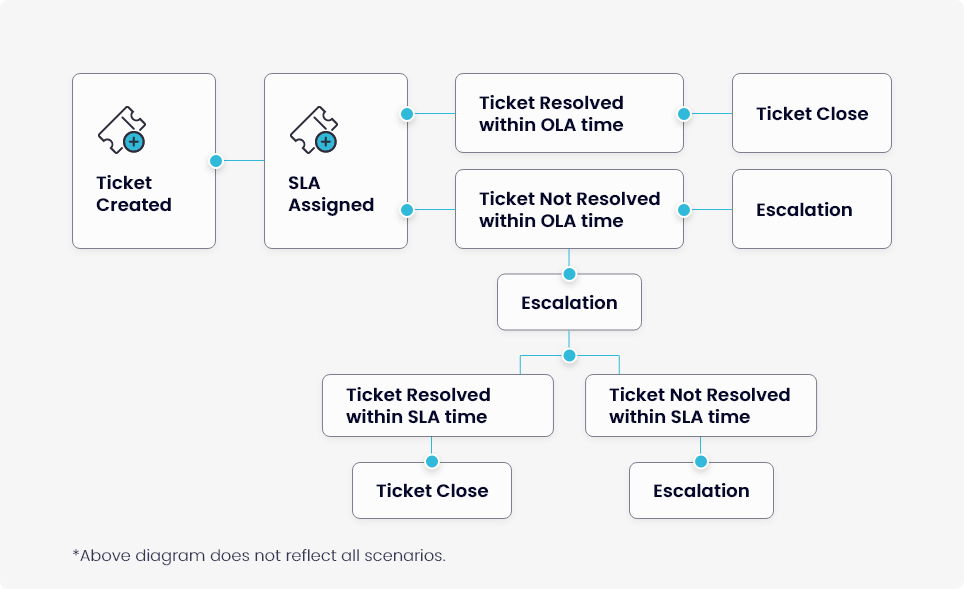
We don’t differentiate between OLA and SLA in our product from a functional point of view. OLAs are part of SLAs. The below diagram reflects how OLAs work in conjunction with SLAs.
Response Time: Response time is the time for a technician to respond.
Resolution Time: It is the maximum time needed to resolve a ticket.
Total OLA Time: Total OLA time is for internal teams to resolve the issue.
Total SLA Time: Total SLA time is the time agreed between a service provided and a client to resolve the ticket.
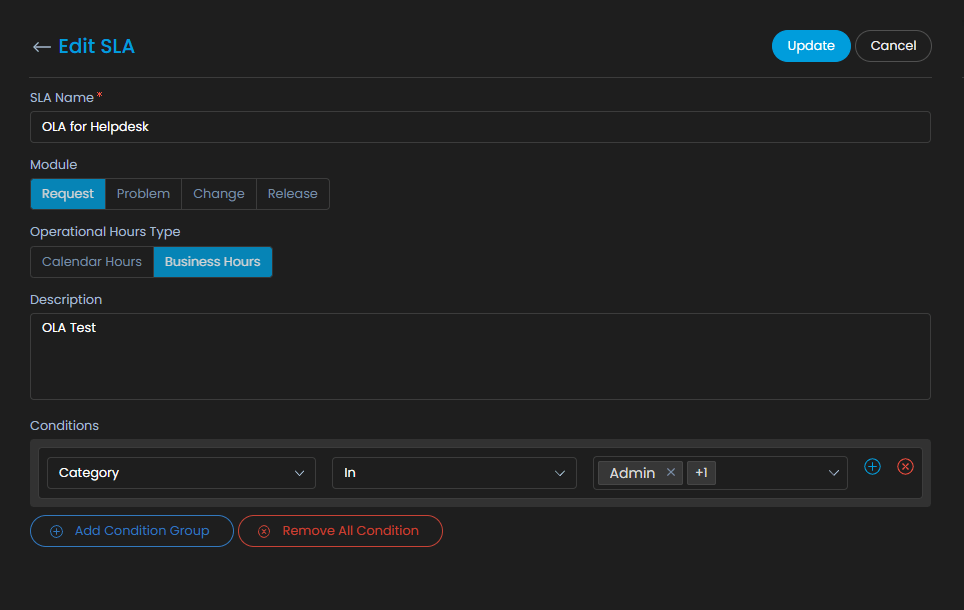
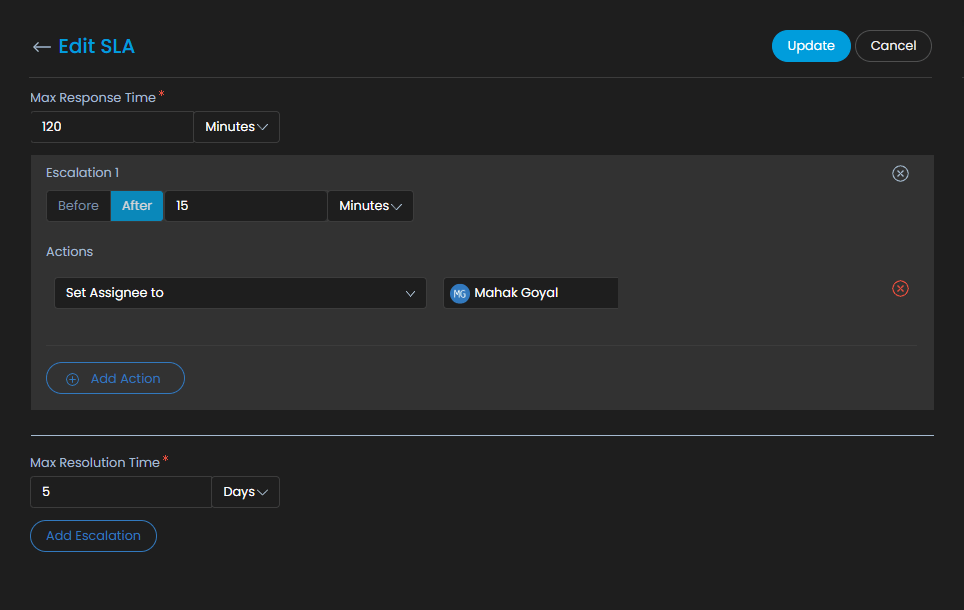
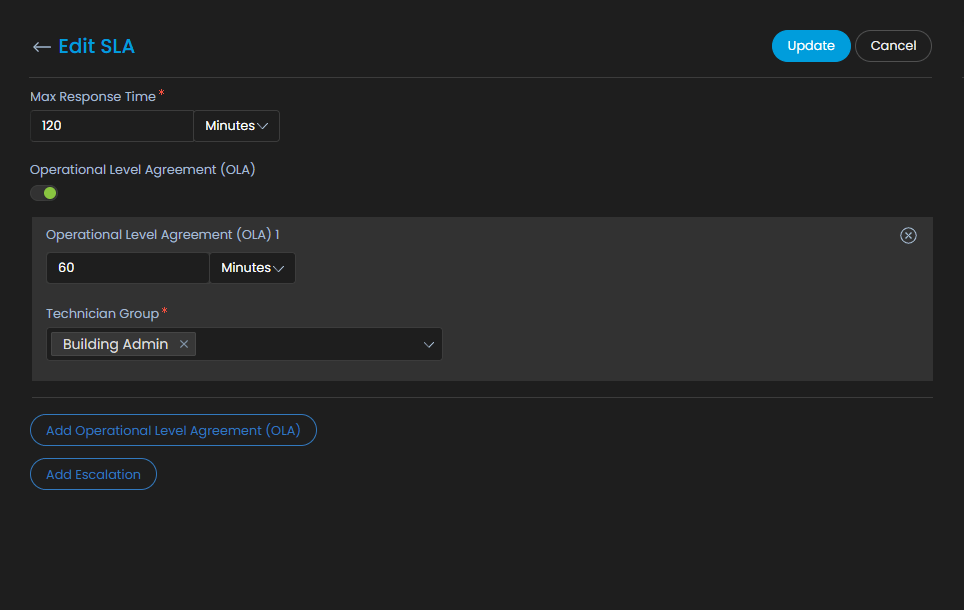
Steps involved in defining an SLA
SLAs are created with conditions and escalation criteria along with an option to define OLA. Here are the steps involved in creating an SLA.
Set Operation Hours:
Before setting up an OLA it is essential to mention operational hours.
Define Service Agreement:
Once the operational hours and conditions are defined, the next step is to define the service agreement.
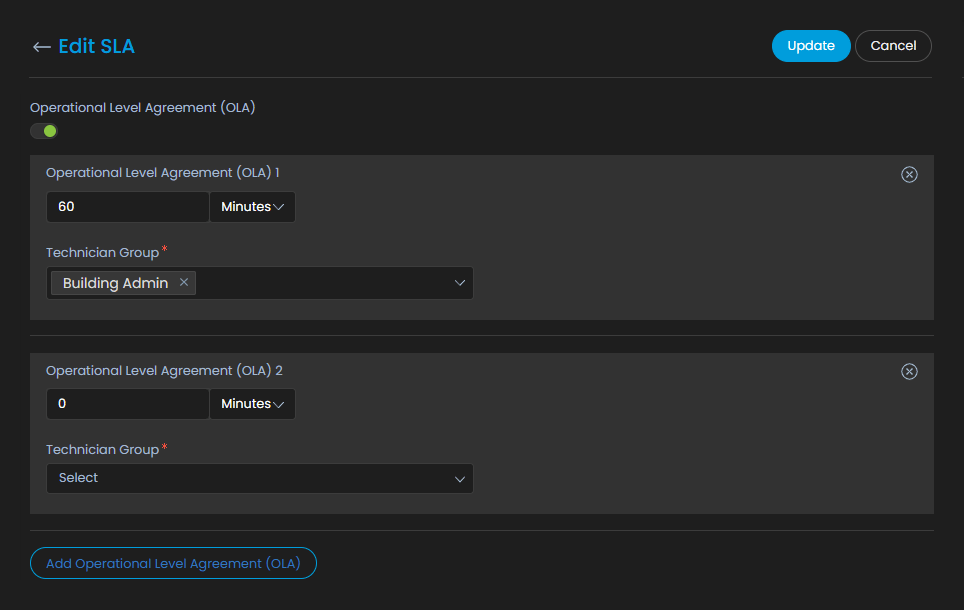
Define OLA:
Once the conditions are mentioned OLA needs to be defined.
Activate Agreement:
Hitting the create button automatically activates the SLA along with the OLA.
How OLA Will Work In The Event Of A Breach?
SLAs are created with conditions and escalation criteria along with an option to define OLA. Here are the steps involved in ServiceOps makes services accessible from the portal. Whenever a ticket is created, an SLA is assigned based on the conditions defined in the SLA. This means the following: eating an SLA.
- Ticket must be assigned within a defined time.
- In case SLA has an OLA, the resolution must happen within the timeframe defined by OLA.
- Since OLAs are for internal teams, OLA violations wouldn’t affect the end clients. But the ticket must be resolved within the total SLA time to prevent a breach of the agreement.