What is an Enterprise Network?
An enterprise network serves as the communication backbone of an organization. It facilitates the connection of computers and related devices across various departments and locations.
This infrastructure enables internal and external communications, aking data exchange and resource sharing essential for business operations.
How Does Enterprise Network Work?
The Enterprise Network integrates components such as endpoints, network devices, and communication protocols to ensure efficient and secure data transmission within the organization. Users can access shared resources, applications, and data from any location through the enterprise network.
Specialized switching and routing devices effectively manage crucial business information flow. Enterprise networking solutions provide connectivity across multi-cloud and hybrid networks, streamlining operations and enabling network automation.
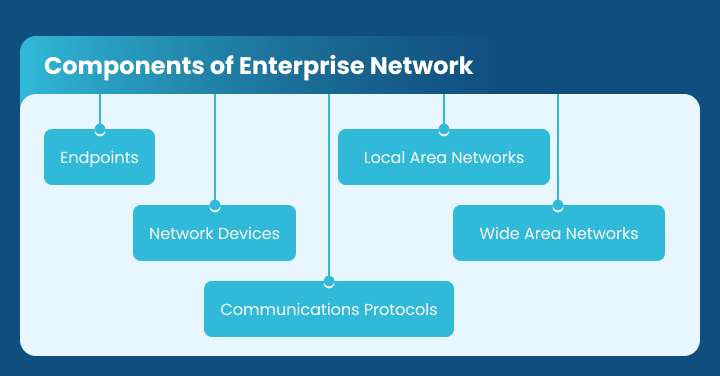
Components of Enterprise Network
The components of an enterprise network comprise:
- Endpoints: These are the devices, including mobile devices, systems, and servers, connected to the network to send, receive, and process data.
- Network Devices: This category encompasses bridges, routers, switches, firewalls, and storage devices responsible for managing and controlling the data flow within the network.
- Communications Protocols: These are the rules and conventions governing communication between devices in the network, ensuring seamless data exchange while maintaining security.
- Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs connect devices within a limited area, such as a building or office, allowing direct communication between devices.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs extend the network’s reach across larger geographical areas, connecting different office locations or branches to facilitate communication and resource sharing.
Benefits of Enterprise Network
Implementing an enterprise network comes with several advantages:
- Better Communication: It makes communication easier among the organization’s users, devices, and applications.
- Sharing Resources: Enterprise networks allow the efficient sharing of resources like data, applications, and storage, making the most out of what’s available.
- Centralized Data Management: They offer a central hub for managing and securing the organization’s data, ensuring it stays safe and accessible.
- Improved Collaboration: Enterprise networks encourage teamwork among users and systems, which boosts productivity and sparks innovation.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By simplifying connections and resource use, enterprise networks make operations more efficient, saving time and money.
- Secure and Scalable: They provide a safe and flexible platform for the organization’s growth and tech advancements, keeping data private and meeting regulations.
These benefits work together to make the organization perform better and stay competitive.
Enterprise Network Architecture
Enterprise network architecture refers to a network’s design, structure, and layout. It involves organizing various components, connections, and communication protocols.
This architecture is crucial for managing essential business assets and supporting tasks like VoIP, data storage, and analysis.
System administrators use visual tools to understand network components such as switches and routers. The architecture ensures that all network components are interconnected to deliver services efficiently.
The architecture of an enterprise network comprises distinct yet interconnected domains, including:
- Internet of Things (IoT), Branch, and Campus: This domain covers the organization’s interconnected devices, branches, and campus networks.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs connect devices across larger geographical areas, facilitating communication between office locations.
- Data Center and Hybrid Clouds: This domain focuses on the organization’s centralized data storage and hybrid cloud infrastructure.
This structure is essential for supporting business-critical assets and tasks such as VoIP, data storage, and telecommunications systems.
It enables system administrators to gain insights into various network components, ensuring all elements are interconnected to deliver services.
Monitoring Enterprise Network Performance
Monitoring the performance of an Enterprise Network is crucial for its smooth operation. Several methods are used for monitoring:
- SNMP-based Monitoring: Utilizing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) to monitor and manage network devices and their functions.
- Passive Analysis: Collect and analyze network traffic data without interrupting its flow to gain insights into performance and security.
- Active Monitoring: Proactively testing and monitoring network components and connections to detect and resolve potential issues before they impact operations.
Managing Enterprise Network Device Configuration
Network configuration management involves organizing and maintaining information about all network components. It encompasses tasks such as:
- Network Device Discovery
- Inventory Maintenance
- Configuration Backup
- Monitoring Configuration Changes
- Compliance Tracking
This process is crucial for maintaining accurate network configurations and avoiding potential outages within the network. Many organizations prefer using network configuration tools to simplify the management of a large number of connected devices.
These tools offer features such as:
- Automated backups of configuration files
- Real-time tracking of configuration changes
- Encryption and storage of configuration files
- Recovery from network disasters
- Automation of simple and complex network operations
- Reduction of configuration errors
- Time-saving on repetitive tasks
- Generation of detailed reports on changes, inventory, compliance, and other network parameters
- Provision of role-based access control
These features enable system personnel to efficiently manage network components, reduce downtime, ensure compliance, and improve visibility and accountability.