Take the Proactive Approach with ITIL Problem Management
Motadata ServiceOps ITSM Platform’s Problem Management can help you Reduce Repetitive Disruptions Occurring in the IT Infrastructure and Improve Customer Satisfaction.
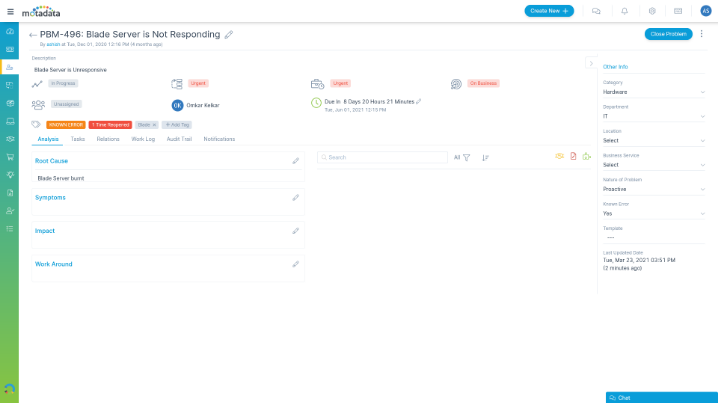
Eradicate Recurring IT Issues with Root Cause Analysis
Get greater visibility into systemic issues by identifying and diagnosing root causes of recurring incidents.
- Record symptoms and analyze the impact
- Provide temporary workarounds or solution
- Maintain known error records
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Service Availability
- Improved User Satisfaction
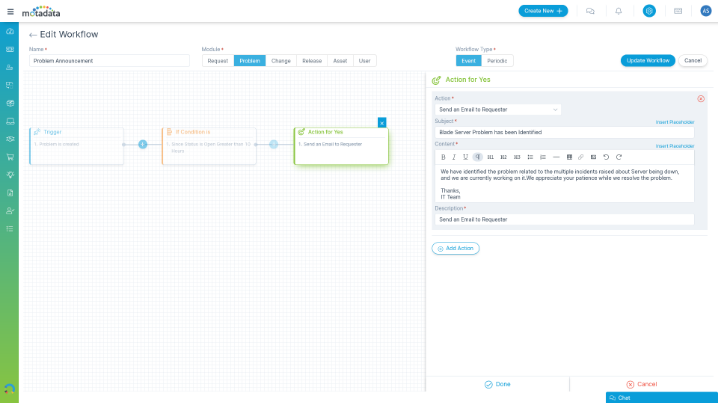
Accelerate Resolution Process with Workflow Automation
Efficiently manage problems by automating low-level tasks with multi-level event-based or periodic workflows.
- Automate changing of status on tickets based on pre-defined conditions
- Automatically trigger the closure of linked incidents when the associated problem is closed
- Automate announcements on problems to prevent incident duplication
Key Benefits
- Improved ROI
- Faster Responses
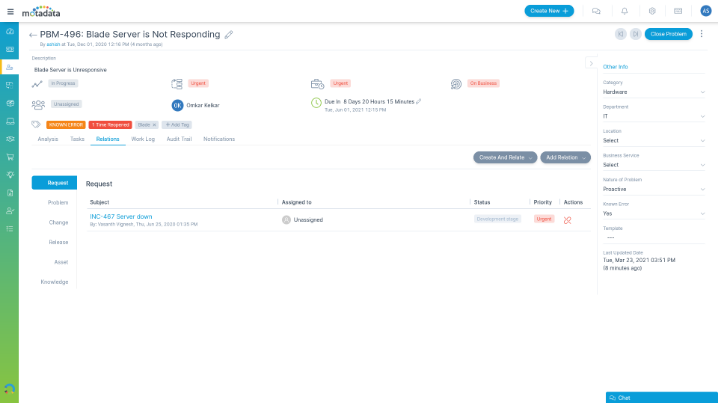
Easily Integrate with Other ITSM Processes
Ensure high service availability by cohesively using problem management with other ITSM processes like incident, change, knowledge, and asset management.
- Link similar incidents to a problem
- Implement a change on identifying a permanent solution for a problem
- Publish knowledgebase articles for future reference
Key Benefits
- Increased Operational Efficiency
- Better Visibility
Improve Your
Service Operation By 30%
Other Features
Eliminate Recurring Incidents and Minimize Disruptions to Ongoing Business Operations with our Problem Management Software.
Ebook
IT Service Desk, A Complete Guide
A Guide to Supercharge your IT Service Delivery.
Explore ServiceOps
An IT Service Management Solution that is Easy to Use, Simple to Set Up, and has Everything you need to Provide a Seamless IT Service Delivery Experience.
Try ServiceOps for 30 Days
Download our software free of cost for 30 days
Schedule Demo With Our Expert
Book a slot in our calendar and experience ServiceOps live.
Do You Have Any Questions? Please Ask, We Are Ready To Support
If your question is not listed here, please feel free to reach out.
There are a few techniques to establish a successful problem management process. First, define and document the scope of the process and define roles and responsibilities. Then, identify and clearly define reactive and proactive triggers.
Make sure that you understand the difference and relationship between incidents and problems and establish an effective incident management process. Use the “5 Whys” technique. Offer a known error database for efficient problem handling and use problem management cohesively with other ITSM processes to produce more value.
Finally, ensure that you have well-defined KPIs and a clear management reporting process.
There are two types of problem management processes – proactive and reactive problem management.
Proactive Problem Management focuses on detecting future incidents and preventing them from recurring by identifying and eradicating the root cause before they have the potential to cause service disruptions.
Reactive Problem Management focuses on responding to repetitive incidents by determining the root cause and recommending a long-term solution. It is critical to recognize these recurring incidents as problems, in this case.
So, proactive problem management is commenced in service operations but is generally regarded as part of continuous service improvement and aims to identify problems and prevent incidents from occurring at all, whereas reactive problem management is implemented as part of service operation with the aim to follow-up on the incidents that have already occurred.
The problem management process helps in identifying and understanding the root causes of an incident and determining the best approach to eradicate that root cause.
The problem manager oversees the overall process of resolution for a particular problem. They organize and direct all aspects of the problem resolution effort comprising of assembling the appropriate teams, tools, and information.
The responsibilities of problem managers include managing the problem lifecycle, averting incidents from occurring, reducing the impact of incidents, providing interim solutions or workarounds for incident management, producing definitive solutions for known issues, as well as performing trend analysis.
Implemented in the right way, problem management can provide great value for your organization. It increases the first-time resolution rate by providing permanent solutions to incidents rather than just stopping at workarounds. This way the problem management process reduces the impact of incidents on ongoing services and prevents almost all recurring incidents to boost user productivity.
Problem management helps refine the service design by identifying root causes to ensure effective service delivery and strengthen the confidence of users. It helps eliminate the errors in an organization’s services through suitable documentation and decreases the time it takes to recover from these failures through systematic maintenance of a knowledge base.
