IT infrastructure management has become one of the key components for the smooth operation of businesses in the rapidly evolving digital era.
It has become crucial for businesses of all sizes to adopt a reliable IT framework that can handle the growing modern business complexities.
The global IT Infrastructure monitoring market will reach a whopping amount of $21.72 billion by 2034.
Thus, to ease day-to-day operations and enhance productivity and growth, it is necessary to implement best practices for IT infrastructure.
The physical devices in an organization, including storage systems, servers, routers, network infrastructure, and software components like databases, operating systems, and cloud computing, are a few key elements of an effective IT infrastructure.
By leveraging these services, you can achieve your business goals, enable seamless communication and efficient workflow management, and enhance scalability.
By implementing best practices in IT infrastructure management, your organization will not only improve system performance and productivity but also ensure data security and keep you updated with technological advancements.
Let us have a look at some of the best practices for IT infrastructure that can help you attain optimal performance.
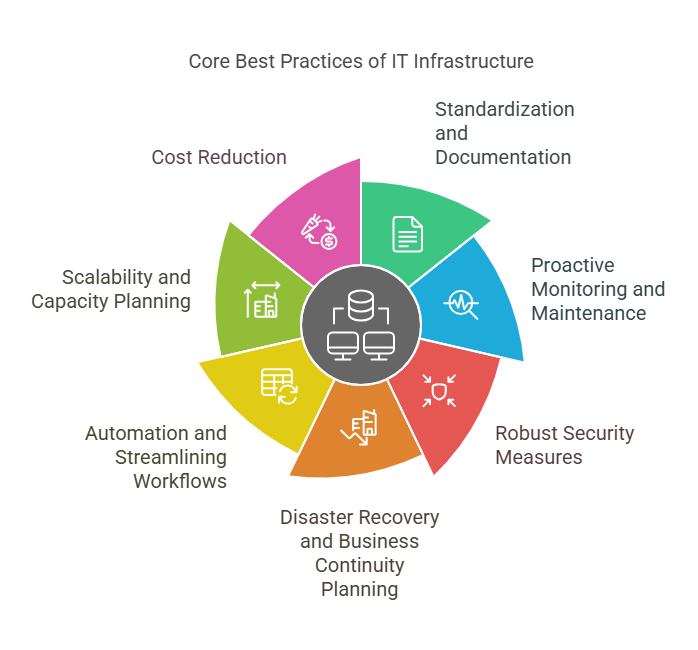
What is the Core Best Practices of IT Infrastructure?
Businesses must understand that the IT landscape is expanding at a rate of knots, and if they do not evolve their process, they are going to lag their competitors.
Thus, to make more informed business decisions, it is essential to understand the core best practices of IT infrastructure.
1. Standardization and Documentation:
Standardizing your hardware and software, as well as documentation, is crucial for efficiently managing IT infrastructure.
By standardizing your processes and configurations, you can simplify your management process and troubleshoot issues much faster.
Further, documenting your configurations allows team members to maintain consistency and streamline all operations.
Team members even find it easier to identify and resolve issues with standardized processes as they do not have to sort each component and manage their complexities.
With proper consistency and quick resolutions, IT teams can reduce the complexities and better manage IT processes.
Large organizations with multiple systems often find standardization essential to ensuring interoperability between different systems.
Clear documentation also helps reduce third-party integration issues and ensures seamless operations with smooth communications.
Another benefit of clear documentation is that it acts as a point of reference for team members and enables them to minimize downtime.
Further, it can be used for compliance requirements and audits.
2. Proactive Monitoring and Maintenance:
Implementing proactive monitoring is essential for any organization that wants to maintain optimal Information technology infrastructure performance and prevent issues from escalating and damaging goodwill.
With continuous monitoring, users can keep track of their server uptime, data center, cloud storage, resource utilization, network status, application performance, and other key metrics.
Watching a constant eye on these critical metrics helps identify anomalies at an initial stage.
You can also invest in various monitoring tools and APM solutions to gain real-time insights and ensure minimal disruptions to operations.
Further, ensuring preventive maintenance strategies is equally important for maintaining the health status of an IT infrastructure.
By maintaining hardware components, running software patches, and generating data backups, you can prevent downtime, excessive costs due to system failure, and protection against vulnerabilities.
Regular maintenance further allows timely replacement and repair of outdated hardware components before they affect performance, thus ensuring continuity at all times.
3. Robust Security Measures:
With the rising cyberattacks and data breaches, it has become highly crucial for organizations to implement security measures that ensure full-time protection of IT infrastructure against potential threats.
Cyberattacks can not only result in financial issues but also cause reputational damage. Hence, incorporating robust security practices is a necessity for maintaining business continuity.
You can deploy firewalls, run regular audits, and incorporate intrusion detection systems, data encryption practices, user access controls, and other security measures.
Firewalls will help prevent untrusted external networks from accessing your data and block unauthorized access. IDS solutions, on the other hand, will help keep track of suspicious activity or behavior in real-time.
With data encryption, you can encrypt all your data in transit or at rest, thus preventing unauthorized users from reading the crucial information.
Similarly, by implementing role-based access control and multi-factor authentication, you can ensure better security of your data.
4. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning:
Fostering a robust disaster recovery plan will not only help your business recover to its original state in less time but also guarantee that your essential services will remain available without any loss.
A Disaster recovery plan is crucial for IT Infrastructure resilience. Be it power outages, natural disasters, hardware failures, or cyber threats, you can recover in all states by implementing this strategy.
It helps you maintain regular data backups, runs thorough risk assessments, follows strict procedures and technologies for quick restoration of IT systems, and more.
Without this plan, you might face data loss issues and extended downtime which will eventually affect your IT operations and income.
Additionally, you must prepare for a comprehensive business continuity plan, a broader approach that aims at maintaining operational functionality at all times with fewer or no disruptions.
In this approach, you must establish communication protocols, proper coordination among stakeholders, and maintain up-to-date documentation.
With disaster recovery and business continuity plans, organizations can reduce downtime and maintain resilience.
5. Automation and Streamlining Workflows:
Automating routine tasks can be highly beneficial for IT infrastructure as it will eliminate human errors as well as improve your efficiency level.
There are several IT infrastructure monitoring tools that come with built-in automation features, enabling quick management of repetitive tasks, reporting, provisioning as well as patching.
With this feature in hand, your IT team can focus on other complex problems. Software upgrades are implemented regularly and swiftly, for instance, thanks to automatic patch management, which lowers the possibility of security flaws.
It further helps streamline your workflows, i.e., simplifies the whole process of managing complex issues and reduces bottlenecks.
You can map out your workflows and identify inefficiencies in real-time. Further, the workflow automation tools help standardize IT processes and ensure workflow efficiency.
6. Scalability and Capacity Planning:
Scalability and capacity planning are essential elements for ensuring your IT infrastructure grows smoothly.
Scalability allows IT teams to gain an idea that they can expand effortlessly with the increasing demand or support for new services and applications.
Capacity planning, on the other hand, looks after the resource availability to meet future business needs.
Under capacity planning, you must assess your existing physical resources and their usage, forecast for future requirements and implement strategies for better resource allocation.
There are several capacity management software available in the market that can assist you in monitoring performance, analyzing trends, gaining insights, and identifying bottlenecks.
Through the use of virtualization and public cloud services, you may optimize performance and reduce costs by dynamically adjusting resources in response to changes in workload.
When these procedures are followed, your infrastructure will be able to easily adjust to changing requirements and support your business objectives.
7. Cost Reduction:
Another key practice that you must look after is cost reduction for it directly impacts the organization.
By optimizing IT infrastructure, you can reduce your costs, which only requires proper utilization of cloud services, allocating resources effectively, and scaling as necessary.
Further, implementing some of the above-listed practices like standardization, timely maintenance, and automation can also help with cost management.
Another method to reduce costs is to make maximum use of open-source software where applicable.
Budget-conscious businesses find open-source solutions appealing because they frequently offer strong capability at a small fraction of the price of proprietary software.
Furthermore, by paying for resources through subscriptions and avoiding the capital expense linked with on-premises infrastructure, cloud-based solutions can provide enterprises with cost-effective scalability.
Additionally, you can optimize your resources using virtualization and containerization methods.
Businesses can minimize operating expenses and the requirement for additional physical servers by optimizing the utilization of physical hardware resources.
Proactive maintenance techniques, such as routine upgrades and preventative inspections, can also increase the longevity of IT assets and decrease the need for expensive repairs and replacements.
Conclusion
Organizations can no longer rely on traditional IT infrastructure practices and methods to compete with one another in the evolving digital era.
It is time to incorporate modern practices, work on the key components of IT infrastructure for smooth business operations and end users experience.
By implementing the above-listed best practices in IT infrastructure management, you can ensure efficiency and resilience.
Hence, make sure to standardize the key components of an IT infrastructure for quick troubleshooting. Proactively monitor and run audits for optimal IT performance.
Further, implement robust security practices to protect IT services against cyber-attacks.
At the same time, you can implement disaster recovery and business continuity planning to reduce business downtime.
Additionally, automation and streamlined workflows will help improve overall efficiency and reduce human errors. Scalability and capacity planning are also crucial.
Lastly, techniques for cutting costs, such as using open-source software and making the best use of available resources, support the financial viability of a company.
There are even trusted IT infrastructure monitoring tools in the market like Motadata that can help you build a robust and resilient IT infrastructure.
The AI-driven monitoring tool will offer deep visibility into the entire infrastructure as well as alert on all suspicious events across your hybrid infra.
You can even monitor your cloud services, local area networks, and system resources using this powerful tool.
Further, you can use these trends for competitive advantage and gaining real-time insights for better optimization.
FAQs
With more and more businesses adopting digital technologies, infrastructure is becoming a critical part of this equation. IT infrastructure is becoming more cohesive but also more complex due to a number of quickly developing techniques and technologies, such as server virtualization, hybrid cloud, software-defined networking (SDN), and more.
With an IT infrastructure strategy, you can outline some of the best practices and methods for efficiently managing IT resources. It may include plans for cost control, security, standardization, and alignment with business goals.
When an organization’s IT infrastructure is well-defined, it can support its objectives and adjust to the rapidly changing business and technology landscape.
Hardware, Software, and Networking are the three primary IT infrastructure components. Hardware covers all the physical devices, such as your computer systems, servers, data storage systems, whereas, software includes all software applications, operating systems, programs, and management tools.
Network, on the other hand, includes the different connectivity components, for example, routers, switches, and communication protocols that allow smooth data exchange within the complex IT environment.
There are several key performance indicators (KPIs) that an organization can use to measure the effectiveness and success of IT infrastructure practices. For example, system uptime provides insights into the percentage of time spent using and accessing IT systems.
Secondly, Incident Response Time updates how much time a user takes to identify, respond, and resolve an IT issue. Resource utilization is another key metric that plays a key role for it enables users to understand the efficiency of hardware and software resource usage.
Lastly, security incidents provide insights on the severity of security breaches and vulnerabilities.