Many businesses use the cloud infrastructure to save on the maintenance cost of physical hardware and other expenses.
Further, it provides organizations various services, from computing power to storage, to help them stay competitive and flexible.
Too much competition in the market results in the adaptation of more and more technology, eventually leading to excessive data. You can no longer rely only on devices to store large volumes of data as it won’t be enough and can result in fraud and breach.
By moving all their data to cloud resources, businesses can add a sense of security and save business from excessive expenditures.
In this blog, we will discuss cloud infrastructure in detail covering all its benefits and drawbacks for business.
Significance. Further, we will explain how the cloud infrastructure works and examine its crucial role in cloud computing.
We will also explore the key components, Cloud Infrastructure Delivery Models as well as future trends that enterprises must take into account.
What is Cloud Infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure is a distributed system that includes all the components essential for cloud computing, such as servers, storage, networking, and virtualization software.
It refers to the hardware and software components that play a key role in delivering cloud computing services to a large audience over the Internet.
Businesses have to no longer own and maintain physical hardware with this pay-as-you-go cloud model, resulting in better management and operation of their computing services.
How Cloud Infrastructure Works?
The cloud is a decentralized place owned and managed by cloud service providers.
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are some of the top cloud service providers with large data centers.
Each cloud application has a hosting company that maintains the enormous data centers and offers security, storage space, and processing power essential for smooth functioning and operations.
To ensure uninterrupted performance and robust security, many businesses rely on DDoS Protected VPS Hosting, which safeguards their applications from malicious attacks while maintaining optimal speed and reliability.
It even supports the virtualization method that helps abstract resources from the physical hardware they are usually placed on and move them into the cloud.
With cloud infrastructure, businesses have to no longer manage and maintain physical hardware.
Role of Cloud Infrastructure in Cloud Computing
In cloud computing, cloud infrastructure plays a key role as it helps in the easy deployment and scaling of all data, applications, and services over the Internet.
It helps businesses store and manage their data in large-scale data centers that can be easily accessed by any authorized user, regardless of their location.
Also, users gain access to scale their cloud resources as per their needs, unlike local devices and physical servers.
Additionally, earlier businesses faced the problem of maintaining the traditional infrastructure setup, however, with the cloud computing infrastructure, you only have to pay for the resources you use.
Top Components in Cloud Infrastructure
There are several key components in the cloud infrastructure optimized for specific needs, including:
- Servers – In the cloud, you gain access to virtual servers rather than physical servers that help businesses maintain and store all their applications and data.
- Cloud storage – Instead of storing your sensitive information locally or on the device, the cloud storage component allows businesses to keep their data remotely, on servers that are reachable via the internet. Also, it is scalable which means businesses can add or limit their storage space as per the need.
- Networking – Using software-defined networking equipment, businesses can manage and configure both physical and virtual networks. Also, you can connect your network with other cloud infrastructure components, such as servers, resulting in quick and secure data transfer.
- Hardware – This includes the physical servers, storage units, and networking hardware that comprise the cloud’s foundational architecture.
- Identity and Access management system (IAM) – User account creation and management, permissions setting, and policy enforcement all come under this component of cloud infrastructure.
Why is Cloud Infrastructure Important?
As the businesses are expanding, so are their services and data management requirements.
It has become important for businesses to invest in cloud infrastructure solutions to host their applications and store data on a large scale.
The cloud infrastructure solution provides the ability to use computer resources on demand without having to buy and maintain physical hardware thanks to the pay-as-you-go cloud model.
Further, by enabling the quick deployment of new services and applications, cloud infrastructure promotes innovation by enabling a dynamic and adaptable digital ecosystem.
3 Main Types of Cloud Architecture
Cloud infrastructure comes in various forms, each with unique properties and applications.
But the most popular kinds of cloud infrastructure are as follows:
1. Public Cloud – This cloud infrastructure is generally owned and maintained by third-party cloud services providers like Google Cloud Platform and Amazon Web Services.
Public cloud services are cost-effective, offer robust security measures, and make their servers, networks, and databases available to the public via the Internet.
Also, they have the least control over the infrastructure compared to other cloud infrastructure types.
2. Private Cloud – Unlike the public cloud, the private cloud architecture is owned by a single company or a third-party provider. Also, the level of control and cost is higher than public clouds.
3. Hybrid Cloud – It is a combination of the public and private clouds, i.e., comprises the properties of both clouds.
It allows you to keep control and security of your private clouds while benefiting from the cost and scalability features of public clouds.
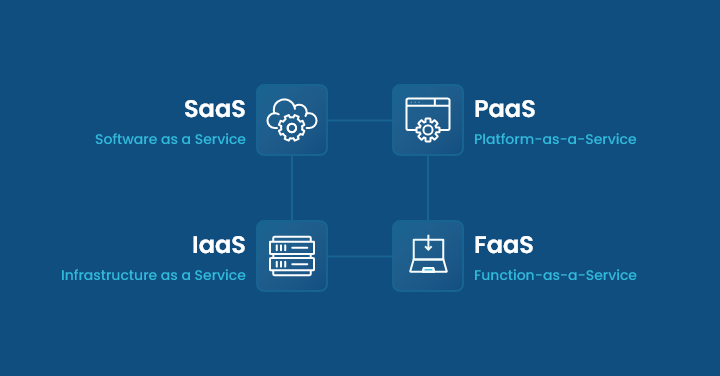
3 Cloud Infrastructure Delivery Models
Three models are available for delivering cloud computing services, each representing a different level of resource provision and access.
1. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
In the IaaS model, businesses use a dedicated internet connection to access cloud infrastructure components as resources.
It incorporates cloud service providers offering their clients virtualization, servers, data storage services, and other resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
There is no longer a requirement for an expensive, on-site installation because the cloud service provider maintains all networking infrastructure and data storage servers.
For example, AWS and Google cloud platforms.
2. Platform as a service (PaaS)
Organizations can create software without having to worry about maintaining the backend environment thanks to the platform as a service computing architecture.
In addition to providing additional development tools like storage resources, load balancing, autoscaling, automated deployment functionalities, compilation services, and version control, PaaS providers customize environments to meet the specific requirements of each tenant.
3. Software as a service (SaaS)
Unlike IaaS and PaaS models, this model does not involve clients directly utilizing cloud infrastructure-based resources.
IT personnel are not required to engage in management or maintenance because end users may simply access the cloud application using a web browser or mobile device. OneDrive and Dropbox are some examples of this model.
Also Read: Types of Cloud Computing Services
What are the Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure?
A strong cloud infrastructure is essential to the success of cloud computing.
Here are a few benefits of having a robust cloud infrastructure for your company:
1. Better Automation
When using an internal IT infrastructure, a specialized IT team must oversee, manage, and handle all IT-related tasks.
Integrating updates or modifications to the current infrastructure is another team’s responsibility.
This takes a lot of time and money, and there is a better option with cloud computing.
Cloud providers regularly upgrade their security and feature sets to ensure that their servers meet the highest industry standards.
For your startup, each of these changes becomes instantly available.
Additionally, to guarantee peak performance, cloud providers completely manage and maintain servers.
Since apps on the cloud are automatically optimized, this makes software integration easier.
2. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Cloud providers offer their clients all-inclusive, rapid, and affordable disaster recovery options.
Cloud computing is the best option for startups that cannot afford prolonged downtime.
3. High Data Security
A single server is often used to synchronize enormous amounts of data, raising security problems.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, has simplified and increased security since it offers an extremely sophisticated security feature that guarantees application security and data protection.
To guarantee secure communication and better data over networks, it also offers authentication and encrypted data, reducing the hassle of a data breach.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing increases flexibility, i.e., without making an investment in physical infrastructure, you may easily scale up resources and storage to match business demands.
Businesses do not have to invest in or construct the infrastructure to handle their maximum traffic levels.
Similarly, if resources are not being properly used, they might swiftly reduce in size.
Drawbacks of Using Cloud Infrastructure
No doubt there are several benefits to cloud infrastructure, but at the same time, it comes with a few drawbacks, such as
1. Limited control: When you rent resources from a third-party provider, you might be somewhere giving up some control over the underlying hardware and software.
Certain technologies or protocols may have constraints placed on you, as well as limitations on customization and setup.
2. Complexity: For businesses that are unfamiliar with cloud computing, managing a cloud infrastructure can be challenging. Proper training and experience are essential for managing and maximizing cloud resources.
3. Internet dependency: Another drawback of Cloud infrastructure is you are completely dependent on the Internet to access its benefits.
Also, the Internet is susceptible to traffic jams and network failures. Performance issues or a short lack of resource access may arise from this.
What are the Top Cloud Infrastructure Providers?
Here are some of the top cloud infrastructure providers in the market you can rely on for great results, including:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS) – One of the popular and oldest cloud infrastructure services in the market that most businesses and individuals opt for, thanks to its excellent features.
It offers access to a wide range of features, including machine learning, IoT analytics, storage, and databases.
2. Microsoft Azure – Another leading cloud service by Microsoft that offers similar features to AWS but focuses more on supporting Windows, .NET, and other Microsoft technologies. It even supports integration with existing Microsoft services.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – It is a Google Cloud service great for businesses with complex networks and developers thanks to its powerful data analytics and machine learning services.
Cloud Infrastructure vs. Cloud Architecture
When a provider offers a wide range of cloud services, the blueprint for a cloud environment consisting of components and services at scale is referred to as cloud architecture.
These are distributed via availability zones, which are remote areas with several physically connected data centers.
It establishes how the different cloud components should be constructed and integrated with one other to satisfy certain needs for apps and other services.
Cloud infrastructure, on the other hand, is a physical representation of these blueprints.
The hardware, virtual resources, and other components of the cloud infrastructure collectively provide computing, storage, and networking services.
In simple terms, if cloud architecture offers a blueprint for the city, cloud infrastructure can be compared to sewage, water, electricity, and transportation networks, as well as communication systems.
Future Trends in Cloud Infrastructure
The development of edge computing, which optimizes performance by lowering latency, will have a significant impact on cloud infrastructure in the future.
We have listed a few more areas that will be trending in cloud computing in the future.
1. Multi-Cloud or Hybrid
Chances are high that multi-cloud will become a trend in the near future.
With time, businesses will become more dependent on public and private cloud services to meet their business requirements.
Hybrid will also be a regular part of use as businesses will move their workloads to the cloud.
So, you might notice both multi-cloud and hybrid cloud deployments in the future. Further, it will strike the ideal balance between cloud security, control, agility, and flexibility.
2. Internet of Things
An important connection exists between the Internet of Things and cloud computing in the future.
Reliable, scalable cloud infrastructure will become more necessary as more and more devices are linked to the internet.
Cloud computing provides the ideal infrastructure for processing and storing the massive amounts of data generated by the Internet of Things.
3. Artificial Intelligence
Businesses and people increasingly use the cloud to store and manage their data due to the rapid improvements in artificial intelligence (AI).
The ability of AI-powered data analytics to spot patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed is one of the primary causes of this.
Furthermore, cloud-based AI systems can learn and develop over time to improve their data processing capabilities.
Consequently, it is anticipated that there will be an even greater need for cloud-based AI services in the upcoming years.
Conclusion
With the growing businesses, management of complex networks, servers, and large databases is less possible locally or on a device.
This is why many businesses opt for cloud-based network solutions or cloud networks for smooth operations and business continuity.
Cloud infrastructure is a collection of these elements (hardware and software) that aid in cloud computing.
It disaggregates their functionalities by hosting the resources and delivering services over the Internet.
With these pay-as-you-go cloud solutions, businesses can save on excessive expenditures and pay only for the resources they use.
Also, It comes with multi-factor authentication and encryption security measures that protect your data in the cloud.
There are several benefits to cloud computing infrastructure, and you can find many trusted tools like Motadata that will help your business in better management of your cloud services and virtual resources.
Further, learn about the upcoming developments and trends in cloud computing in the near future.
FAQs
The main purpose of cloud computing architecture is to provide on-demand access to computer resources such as servers, storage devices, and networking over the Internet without interruption.
It doesn’t require expensive software or hardware expenditures and provides flexibility and scalability. Furthermore, improved security, dependability, and possibilities for disaster recovery are guaranteed by cloud infrastructure.
Consider your company’s demands and specifications before deciding on a cloud service provider. Further, here are a few factors you must keep in mind when selecting a right cloud service provider for your business, such as:
- Look for various security measures, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and other data protection features
- Check if it offers both scalability and flexibility
- Check if it supports pay-as-you-go models and flexible pricing plans
- Make sure it is compliant with the current data privacy laws
- Comes with audit as well as reporting capabilities
Businesses should select a cloud service provider with robust security measures to guarantee data protection and compliance. Sensitive data should have strong encryption and access controls. Additionally, all cloud services must be audited and monitored for regulatory compliance.