Tired of being a firefighter in your IT department who is always battling issues after they erupt? Well, you’re not the only one.
With IT infrastructure becoming more complex day by day, IT managers across the globe face the same challenge.
But not anymore.
Infrastructure monitoring tools are here to save the day by empowering IT managers to not only predict but also prevent IT infrastructure issues.
But how?
In this blog, we will deep dive into the world of IT infrastructure monitoring where we will discuss what infrastructure monitoring is, how it works, its types, challenges, best practices, and factors to considering before choosing an infrastructure monitoring tool
What is Infrastructure Monitoring?
Infrastructure monitoring is a process of tracking and analyzing data collected from IT infrastructure — network devices, servers, containers, virtual machines, databases, etc. to detect and resolve issues, driving higher business outcomes.
Infrastructure monitoring is similar to using a fitness tracker that keeps track of your heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns. Just like a fitness tracker, it monitors the health and performance of your infrastructure, enabling you to take proactive steps to ensure optimal functionality and improve digital operations.
How it Works?
Here, for the sake of simplicity, we are going to explain the working of agent-based infrastructure monitoring.
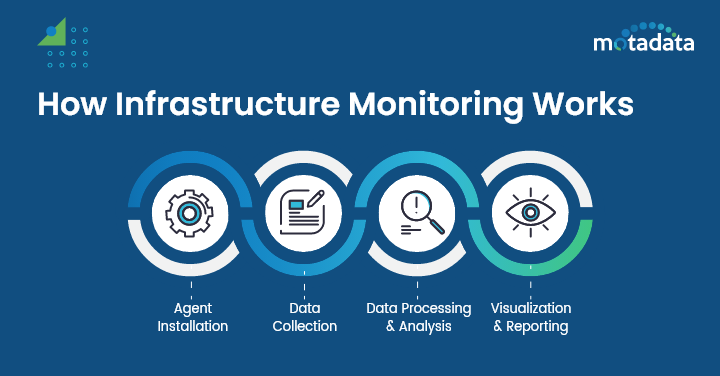
If we look at the working of infrastructure monitoring, the entire process can be broken down into four stages.
Let’s have a look at them one by one.
1. Instrumentation and Agent Installation
It begins with the installation of a software agent on the host. This agent can be either a physical server or a virtual machine. This agent collects data related to:
- Performance
- Availability
- Resource Utilization
2. Data Collection and Aggregation
The installed agent on the host collects various types of data like:
- Metrics
- Events
- Logs
- Traces
Here, Metrics represent aggregated data which gives an overview of the system’s performance.
3. Data Processing and Analysis
The data collected is sent to the backend engine of the infrastructure monitoring solution for processing and analysis.
Here, it processes the data historically and in real-time to offer critical insights into the performance, health, and functioning of the backend components.
4. Visualization and Reporting
Once the data is processed, it is displayed on a dashboard. The dashboard offers a comprehensive view of infrastructure’s performance and status.
This helps the stakeholders to not only monitor but also manage the infrastructure effectively.
Types of Infrastructure Monitoring
There are several types of infrastructure monitoring based on different criteria.
Let’s have a look at them one by one.
1. Based on Monitoring Method
a. Agent-based Monitoring
- It involves the installation of software agents on systems to be monitored for collection and reporting performance and status data.
- This method offers customization in data collection along with alerting based on configured conditions.
- This method also enables continuous monitoring and data collection of systems that are behind firewalls, without any direct network exposure, and when the network connection is lost
b. Agentless Monitoring
- This method monitors performance and status without installing software agents
- It’s a highly efficient and low-overhead method for monitoring a large number of systems
2. Based on Aspect of Infrastructure Monitored
a. Network Monitoring
- Monitors network traffic, devices, and connections to ensure optimal network performance and security.
b. Server Monitoring
- Monitors servers along with memory, CPU usage, disk space, and other server-specific metrics.
c. Application Monitoring
- Monitors software applications by tracking metrics like error rates, response times, etc.
d. Virtualization Monitoring
- Monitors and optimizes virtual machine performance and resource allocation in a server environment.
e. Cloud monitoring
- This involves tracking and analyzing the health, performance, and usage of cloud-based resources and services to ensure efficiency and reliability.
3. Based on Monitoring Focus
a. Performance Monitoring
- Monitors system performance, resource utilization, and response times.
b. Availability Monitoring
- Monitors uptime, downtime, and availability of systems and services
c. Security Monitoring
- Monitors for security threats, intrusions, and vulnerabilities to infrastructure security
Infrastructure Monitoring Challenges
1. Managing Geographic Distribution
Enterprises having global presence have their IT infrastructure, personnel, and cloud services dispersed. This makes enterprise-wide monitoring a tough task.
Also, with several monitoring teams and multiple tools, the correlation of meaningful data becomes a challenge.
Not only this, but also the diverse perceptions of accepted performance across locations leads to inefficiencies and duplicated efforts.
2. Contextual Monitoring for Troubleshooting
Infrastructure monitoring isn’t enough to solve problems effectively.
You need a complete monitoring approach that looks at everything — the systems, the software, how they’re connected, and all the different parts involved.
With contextual insights by correlating data from various components of the system, you can identify the root causes of issues.
These issues could be anything like:
- Using too many resources
- Errors in the software
- Trouble with connections
It’s like solving a puzzle – we need all the pieces to see the whole picture and find the real problem.
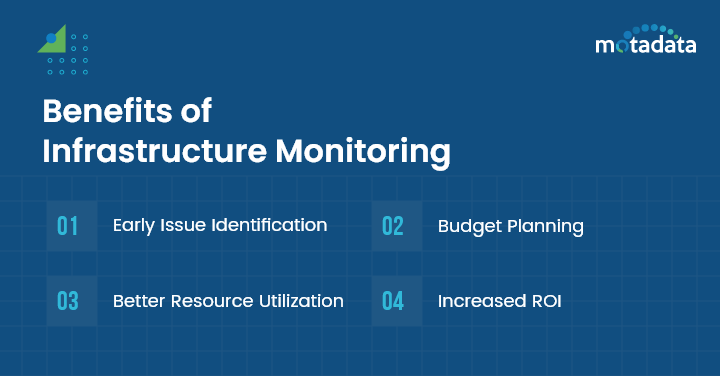
Benefits of Infrastructure Monitoring
1. Early Issue Identification & Proactive Resolution
Infrastructure monitoring tool monitors all the activities taking place throughout the entire IT system in real-time. It enables you to spot problems before they turn into a serious issue.
This gives you the power to proactively resolve potential infrastructure issues before they impact the end-user experience.
2. Budget Planning
Budgeting is a big headache for IT organizations dealing with an ocean of devices.
With infrastructure monitoring, they can anticipate performance issues that may arise in them and maintain an inventory of all such devices which might get replaced in the future.
This visibility and clarity make budgeting easy. Also, it helps IT teams to prepare for any technical requirements and timelines associated with these replacements and upgrades.
3. Better Resource Utilization
Infrastructure offers key insights into system performance by monitoring metrics like:
- CPU Usage
- Memory Utilization
- Network Traffic
- Response Times
These insights help you identify those resources that are underutilized or overutilized.
After that, you can take appropriate resource allocation measures to ensure optimal resource utilization.
4. Increased ROI
Infrastructure monitoring frees up valuable effort and time for SRE and DevOps teams.
This allows them to focus more on their core responsibilities and add more value for the end-users.
Apart from this, these are the other factors that help in increased ROI:
- Enhanced system reliability
- Quicker issue identification
- Rapid resolution
- Minimized downtime
Infrastructure Monitoring Best Practices
1. Collect Relevant Metrics
You often miss a critical insight in the crowd of several metrics data. To avoid this, you must ensure that you are collecting only the relevant metrics.
And to determine the correct metrics, you can:
- Identify metrics to monitor for virtual machines, physical machines, networks, etc.
- Monitor logs and check performance metrics on a regularly basis
- Review the monitored metrics periodically and make changes in the IT infrastructure accordingly
2. Use Automation
Infrastructure monitoring involves far too many checks, making it impossible to be checked humanly. This is why automation has become necessary.
Here, you can leverage the automation feature of your infrastructure monitoring tool to boost your MTTR.
Also, this will enable you to get comprehensive end-to-end observability.
3. Conduct Regular Tests
Testing your infrastructure monitoring tool is critical. Whether you are integrating a new application or starting from scratch, conducting a test run will ensure that everything works just as you intended.
Before you start relying on these tools daily, you must schedule a thorough test to validate their functionality and alignment with your infrastructure needs.
This proactive step ensures that everything works just fine.
How to Choose the Right Infrastructure Monitoring Tool
Here, we have mentioned a few factors which you must consider before choosing an infrastructure monitoring tool.
1. Unified IT infrastructure Monitoring
Your infrastructure monitoring tool must be able to monitor physical, network, storage, and virtual servers, cloud applications, and on-prem applications all at once. Additionally, implementing a secure and private VPN Service ensures that data transmitted between these components remains encrypted and protected from authorized access.
If your tool lacks this capability, you might face problems like:
- Constant tool switching
- Delayed resolution of critical errors
- Need to keep records of multiple licenses
Another thing to look out for is — support for various telemetry ingestion sources and seamless data correlation.
An effective correlation of this data offers meaningful insights which help you to not only identify trends but also to proactively address potential issues.
This eventually leads to faster incident resolution and optimized performance.
2. Support for Multiple Vendors
Today, businesses deal with multiple vendors to meet their diverse IT requirements.
This is why it becomes crucial that your infrastructure monitoring tool supports multi-vendor network endpoints.
Here, you must ensure that your infrastructure monitoring tool has the flexibility to track various infrastructure components irrespective of their vendor.
3. Scalability
If you’re a growing business, you must consider the scalability of your infrastructure monitoring tool.
This is because you don’t want your infrastructure monitoring tool’s performance to degrade as your IT infrastructure expands.
You can determine the scalability factor by asking the below three questions:
- Can it monitor a massive number of applications and devices?
- Can it manage various types of data like metrics, logs, and traces?
- Can it manage a high volume of data without compromising its performance?
Conclusion
As the IT infrastructure keeps on becoming more and more complex, the need for a robust infrastructure monitoring tool becomes essential.
In this article we have covered everything related to infrastructure monitoring from its challenges, best practices, benefits, and a checklist to choose the right infrastructure monitoring tool.
If you feel all this information would put you into analysis paralysis mode, we have a simple solution for you — Motadata AIOps.
With Motadata AIOps’ unified infrastructure monitoring tool, you can perform several actions like monitoring, visualizing, and log indexing on all events across the hybrid infrastructure.
It also comes with advanced features like machine learning-powered alerting and AI classification.
This helps you to adopt a proactive and data-driven decision-making approach to your infrastructure management.
If you want to see Motadata AIOps in action, you can go for a free trial. Or if you’re looking for more information, you can either schedule a demo or contact our experts.
FAQs
Infrastructure monitoring is the process of tracking, analyzing and managing the performance, availability and health of the backend components of a company’s technology stack.
It is important for businesses because it helps them ensure reliable, secure and efficient operations of their IT infrastructure, avoid downtime and service degradation, optimize resource utilization and costs, and improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Infrastructure monitoring works by continuously collecting data from the various traditional and cloud-native components of an organization’s IT infrastructure and analyzing that data to assess the systems’ performance, availability and health.
The two methods for collecting system data are agent-based and agentless. An agent is a lightweight software layer installed by engineers on a host (any system or device that needs to be monitored), which collects relevant telemetry data about the state of the system.
An agentless method relies on existing protocols or APIs to remotely access and gather data from the hosts.
There are several types of infrastructure monitoring based on different criteria. Some of the common types are: based on monitoring method (active or passive), based on monitoring scope (application or infrastructure), based on monitoring domain (network, server, database, etc.), and based on monitoring approach (synthetic or real-user).
While it doesn’t prevent cyber threats, infrastructure monitoring can detect anomalies and unusual activities, allowing for prompt responses to potential security breaches.
Yes, the dynamics differ. Cloud infrastructure monitoring involves tracking resources in a virtual environment, while on-premises focuses on physical hardware within your premises.
Efficient monitoring enhances productivity by minimizing downtime, optimizing performance, and proactively addressing potential issues before they escalate.