Business continuity has become a key priority for most management teams and their IT associates.
Every single minute lost in downtime can result in potentially bloated overheads and reduced revenues.
That said and done, no matter how well-engineered the network is, there will be some issues and problems in its due course of operations.
In the world of IT service management, dealing with these issues efficiently is crucial.
This is where incident management, an integral part of the ITIL(Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework, comes into play.
It’s a structured approach to handling problems promptly and effectively.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of ITIL incident management – from its types and scope to its benefits and best practices.
So, without any further ado, let’s dive into the key aspects of ITIL incident management and see how it can positively impact modern businesses.
What is ITIL Incident Management?
ITIL incident management is a response to any unplanned event or service interruption.
The key objective of ITIL incident management is to restore services as quickly as possible and minimize its impact on the business.
Incident management generally involves several processes of service tickets like:
- Logging
- Classifying
- Prioritizing
- Investigating
- Diagnosing
- Resolving
We’ll have a look at each stage later in the blog.
Defining the First Response to Incident Detection
As soon as an incident is detected, the IT Team’s primary goal is to retain the network efficacy to its normal performance levels, adhering to the SLAs in place.
The IT Team must also record all the incidents that are not resolved immediately.
If an issue of similar nature is recurring, it should be tagged as a problem with a due plan of fixing the systemic errors resulting in the problem’s emergence.
For more extensive enterprise networks, the IT Teams may get overwhelmed by the number and extent of incidents occurring at the same point in time.
Hence, to minimize potential damage, each incident should be ranked in terms of its urgency, significance, and impact on the critical processes.
Incidents that are ranked highly on all three parameters should be immediately addressed.
The Most Important Component in Incident Management – Service Desk
There is a multitude of functions involved in the incident management cycle. The most critical one is the Service Desk.
Without a Service Desk between the users and the IT Team, the latter would be cornered to take up each issue as it is registered.
With this unstructured practice, the IT Team may misallocate resources to marginal issues and miss the more impactful ones.
The Service Desk can act as the interface with the users for collecting responses on the issues.
It can then aggregate the necessary data and prioritize & delegate the resolution process to the IT Team. This way, the process becomes more streamlined, effective, and efficient.
Defining the Roles in the Incident Management Process
1. Primary Technical Support
This team, also termed as the Level 1 Staff, comprises human capital assigned for first-response to incident reports.
They are often members of the Service Desk responsible for capturing and categorizing incidents as logged by the users.
Post this, they work in line with a pre-defined set of instructions to restore services.
If they cannot resolve the issue quickly, it gets escalated to a Secondary or Level 2 Support team.
The primary team might be the first point of contact for incidents, but they do not manage the entire team working on the incident.
2. Incident Manager or Owner
The Incident Manager takes ownership of the entire process – from issue detection to reporting to resolution.
As the issue gets escalated between Level 1 and 2 support team, the Incident Manager takes the responsibility of allocating the incremental resources along with putting together a task-force or a Major Incident Team for working on identified significant incidents.
3. IT Operators
This is the team of individuals who act as buffers in the incident resolution process, ensuring scheduled maintenance of servers, taking up timely data-backups, and monitoring schedule-adherence for critical tasks.
They are also leveraged as additional person-power for a significant incident if and when necessary.
4. Major Incident Team
The team is called in only when the issue has escalated to a severity that will impact the entire enterprise or significant business processes.
A dynamic team is put together in line with the urgency, demanded expertise, and scale of the issue.
Types of ITIL Incident Management Processes
Different companies choose different types of incident management processes as per their requirements.
For instance, some rely on a traditional IT-style incident management process wherever other companies show more trust on DevOps style and Site Reliability Engineer incident management process.
Let’s have a look at each of them one by one.
1. ITIL Incident Management Process
An ITIL incident management process helps an IT team to record, investigate, and resolve service interruptions.
Its main objective is not only to reduce downtime but also to minimize the impact on employee productivity.
The ITIL framework is mainly used by IT teams.
Generally, these teams take whatever they need from ITIL including all types of incidents, issues, and process, leaving the rest.
2. DevOps Style Incident Management Process
In the DevOps incident management process includes three key principles, which are:
- Collaboration
- Flexibility
- Accountability
In this, team members share on-call responsibilities. Also, the members responsible for building the service take ownership of fixing issues.
This type of incident management ensures clear response to incidents by giving strong emphasis on:
- Code Quality
- Documentation
- Standardized Processes
That’s not it! It also focuses on quick response times and continuous improvement via post-incident reviews.
3. Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) Incident Management Process
In this incident process, Site Reliability Engineers (SRE) ensures reliability and availability of online services. To achieve this, they implement the following practices.
a. Service Level Objectives (SLOs)
These are set goals that indicate how well a service should work.
b. Error Budgets
This is basically permitted number of mistakes or problems that a service can have before it’s deemed unreliable.
c. Blameless Post-incident Reviews
As the name suggests, this includes investigation of issues without blaming anyone.
d. Capacity Planning
This ensures adequate availability of resources like data storage and computers for managing expected demand for a service.
The Scope of Incident Management
The scope of incident management covers everything beginning from an end user reporting an issue and ending with a service desk team member resolving the issue.
To understand the scope of incident management, let’s have a look at all the aspects that it covers.
a. Incident Definition
Define the types of IT service issues and interruptions that fall within the responsibility of incident management.
b. Categories
Establish criteria or categories for incidents like:
- Software Errors
- Hardware Failures
- Network Outages
- User-reported Problems
c. Service Impact
Define the scope’s boundaries based on the impact that incidents have on users as well as the IT services.
d. Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Lock in agreed-upon resolution times for various types of incidents.
e. Exclusions
Have a consensus on what types of events or situations won’t be considered as incident within the scope.
f. Continuous Review
Carry out periodic reviews and update the scope to ensure that it remains relevant and adapts to the changing business needs.
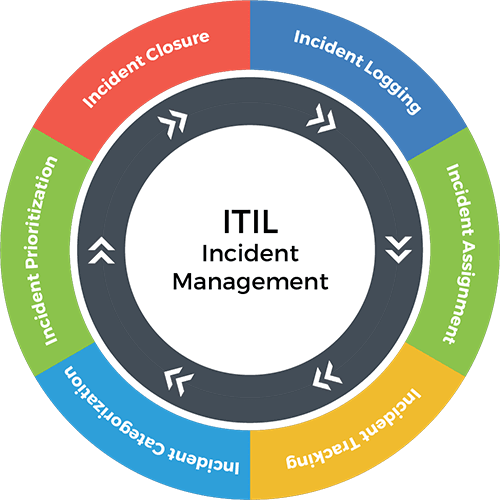
ITIL Incident Management Process
Incident Management process is also a major part of the scope of incident management.
Let’s have a look at the various stages of the incident management process.
1. Identification
An incident can come from anywhere, whether it’s a vendor, customer, employee, or a monitoring system.
Irrespective of the source of the incident, the first step of incident management is incident identification.
For this, you need to include the following:
- Name & ID Number
- Date
- Incident Manager
- Description
2. Categorization
The next step is to assign a logical category to each incident. This categorization helps team to:
Prioritize incidents based on urgency
Swifty find solution if the same incident occurs again
Categorization plays a significant role in problem management as it allows you to analyze the data for patterns and trends.
Also Read: Incident Management vs Problem Management
3. Prioritization
The next step is incident prioritization. For evaluating prioritization, you can assess impact on:
- Business
- No. of people
- Applicable SLAs
- Potential security, financial, and compliance implications of the incidents
Another way of evaluating priority is to determine the relative priority by comparing the incident to every other open incident.
You can also make priority evaluation simpler by predefining the priority levels before an incident occurs.
4. Response
After categorization and prioritization, it’s time to respond.
For this, you can send the incident to the respective teams for troubleshooting. In some cases, the response team fails to find a solution.
In such a scenario, they escalate it to a different team for further troubleshooting.
5. Resolution and Closure
Once every step is concluded, you can now go for resolution by closing the ticket.
Here, you must store all the documentation in a shared workspace that can be used for future reference.
You can also discuss any incident in particular that occurred during the project in the post-mortem project meeting.
This can act as a great transition into the problem management phase.
This phase of the project is significant as it allows you to solve the root cause.
Also Read: 7 Practical Problem Management Techniques to Improve Your Service Delivery
Implementation Benefits of ITIL Incident Management
1. Consistent Service Levels
ITIL incident management addresses and resolves incidents quickly that can otherwise cause disruption in normal business operations.
ITIL incident management process categorizes incidents based on impact and urgency, enabling IT teams in efficient resource allocation and prompt responses.
This approach not only minimizes service disruptions but also ensures adherence of service quality to the established standards.
2. Improved Staff Efficiency & Productivity
ITIL incident management implementation offers clear guidelines that not only streamline workflows but also help IT staff in efficient incident management.
Secondly, knowledge repositories and incident documentation provide all the information that the IT staff need to resolve incidents quickly.
3. Improved User Satisfaction
Timely incident resolution means users experiencing fewer and fewer disruptions.
When this happens consistently, users’ perception towards the IT services becomes positive.
This positive perception can lead to better relationships between the IT team and the rest of the people in the organization.
3 Best Practices for ITIL Incident Management
1. Ensure Effective Communication with Stakeholders
Effective communication with stakeholders throughout the incident lifecycle is a must when you have to handle many complex incidents.
Here, teams must adopt this best practice of communicating the status of the incident right from the moment its first identified to the point when it ends.
This practice not only manages stakeholder’s expectations but also encourages them to follow up if they have any questions or suggestions.
To achieve this seamless communication, you need a documented process framework for the incidents.
This includes:
- The stakeholder
- Preferred method of communication
- Set of technical questions that you must answer before you reach out to the stakeholder
- A templated communication that can be filled and sent
2. Minimize Escalations
More escalations mean more time spent by higher-level teams to resolve incidents.
And that’s not good news, because you want your higher-level teams to focus on more complex issues.
That’s why you must ensure that the maximum number of incidents are managed and resolved by the lowest-tiered tiered teams.
This will not only improve resolution times but also have a huge impact on customers.
To minimize escalations, you can have a documented process that clearly defines:
- How to escalate an incident
- When to escalate an incident
- Who should resolve the escalation
3. Document a Framework for Operational Service Levels
You can identify KPIs to track the performance. For example, you can have metrics like:
- Time to action on critical incidents
- MTTR
- Time to ticket
Along with this, you can ask yourself the questions below.
- Your update frequency is based on what?
- What is the level of severity?
- What are your priorities?
Once this is done, track the metrics. Lastly, you can schedule regular times for analyzing the metrics.
In Conclusion
Incident Management is highly dependent on the Service Desk. It analyses the registering of incidents across categories along with resolution timelines.
Once the incident is processed and closed, the firm can focus on aggregating data to augment the service-quality and take preventive measures to eliminate the arising of incidents in the first place.
While keeping the user at the center of the resolution process, Incident Management ensures that each incident is efficiently resolved, followed by an in-depth analysis and documentation of each incident.
Such rigorous processes ensure that each incident adds to the firm’s knowledge about the loopholes in its systems and creates value by proactively resolving them.
If you’re interested in knowing more about incident management, contact us today for personalized consultation and assistance.
You can also schedule a demo to see how Motadata can help you in enhancing your incident resolution capabilities and deliver exceptional user experiences.
To know more write to us sales@motadata.com.
FAQs:
ITIL incident management is a process that focuses on restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible after an unplanned disruption or incident occurs.
Incident management focuses on resolving immediate issues to restore services, while problem management identifies and resolves the root causes of recurring incidents.
The steps include incident identification, logging, categorization, prioritization, investigation, resolution, and closure.
It ensures a structured approach to managing incidents, reduces downtime, enhances service reliability, and improves the overall user experience.