The evolving digital technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) fundamentally reshape business dynamics. Analyzing the growth and impact of running online businesses, several organizations from different industries started adapting this modern approach to create revenue streams and enhance their customer experience. On one end, it turned out to be a brilliant strategy; on the other, managing the complex business data and systems was a big challenge.
The observability concept has allowed organizations to monitor the internal state of their complex IT systems in real time by analyzing logs, metrics, and traces. Unlike traditional monitoring, this approach helps IT teams gain deeper insights into system behavior, track issues, and troubleshoot them before they escalate. But with IT ecosystems becoming more intricate and interconnected, these basic observability strategies are no longer the best solution. It is time to invest in advanced observability trends to manage security and maintain the performance of dynamic systems.
The year 2025 is expected to encounter major tech trends and rapid AI advancement, raising concerns for organizations to invest in smarter and more proactive ways to monitor and manage their systems.
Observability, which was earlier responsible for only diagnosing problems, will now take on a much larger role—driving automation, enhancing security, and supporting sustainable IT operations. AI-powered insights will make observability more intelligent and predictive, helping organizations prevent issues before they occur. In 2025, Observability will move beyond traditional monitoring.
Organizations that embrace these advancements might gain a competitive edge in managing modern IT environments. The future of observability lies in its ability to provide intelligent, security-driven results, ensure seamless interactions across different platforms, and enhance the end-user experience.
Current State of Observability
In 2023-2024, we tracked several trends showcasing a drastic shift in how organizations approach system monitoring and performance analysis. As per Grafana Labs Observability Survey 2024, 65% of organizations adopted a systematic approach to observability, aiming to prevent issues before they impact users.
Before this, most organizations practiced traditional monitoring, collecting predefined metrics to identify issues. However, the adoption of observability concepts allowed organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of system behavior. Despite recognizing its value, only 10% of organizations achieved full observability.
Various open-source tools, such as Prometheus, Grafana, Jaeger, etc., were also adopted, contributing to a unified observability framework. Prometheus helped collect and store metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, response times, etc., to monitor system health. 85% of organizations also widely adopted OpenTelemetry to help collect different types of observability data, detect issues early, and improve overall system performance.
In complex and distributed systems, tracking requests across multiple services in real time is essential. With distributed tracing, IT teams can monitor request flows and pinpoint performance bottlenecks and failures early. Log aggregation complements this by centralizing logs from various sources, simplifying troubleshooting, and enhancing system insights. Implementing these practices was the need of the hour, but rapid AI advancements demand advanced solutions.
2025 is the year of innovation that will redefine how organizations optimize their IT systems. With the growth of cloud environments and the incorporation of AI practices, companies demand advanced observability tools to understand system behavior and proactively identify issues comprehensively. Here are a few limitations of current observability practices:
Data silos and fragmented insights:
To stay ahead of competitors, organizations invest in multiple monitoring tools which creates data silos – where information is isolated within different systems, making it difficult to get a complete and unified picture of system health. This fragmented data insight makes it difficult for engineers and IT professionals to identify the root cause and overview the system’s health from the same viewpoint.
Challenges in correlating data from diverse sources:
Correlating data from isolated systems can delay issue resolution. Further, team members need to know how to manage different tasks to achieve observability. Over 48% of organizations identify the lack of knowledge among teams as a significant barrier.
Difficulty in predicting and preventing issues:
With increasing complexity, predicting potential system failures without access to advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities is a big challenge. In 2021, only 47% of organizations took more than an hour to resolve production issues. But over the years, this percentage has increased, and 82% of companies reported that their MTTR is now over an hour.
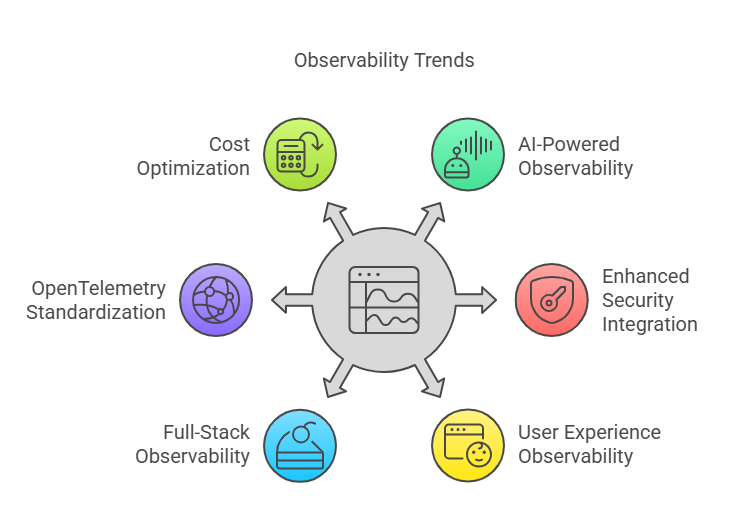
Key Observability Trends for 2025
Today, many organizations plan to optimize their IT costs for better efficiency and monitor overall system performance using observability tools. With modern IT infrastructures becoming increasingly complex, the need for robust observability solutions continues to grow. In 2025, observability is evolving with the integration of artificial intelligence, deeper security insights, full-stack visibility, etc. Let us discuss these observability trends for 2025 in detail.
1. AI-Powered Observability
By incorporating an AI-enhanced observability strategy for your organization, you will introduce predictive analytics and anomaly detection, which will enable IT teams to foresee potential system failures before they occur. Rather than just monitoring your systems, this practice will help predict issues early by spotting odd patterns and unusual behavior. AI-driven tools further enable automated root cause analysis and execution of faster remediation strategies without human intervention.
These machine learning algorithms can constantly analyze vast amounts of telemetry data, improve resource allocation, optimize performance, and reduce downtime. You can enhance your alert settings by prioritizing important alerts and addressing significant problems. These advancements will improve reliability and reduce manual intervention and downtime.
2. Enhanced Security Integration (SecOps Observability)
Cybersecurity threats are also evolving with digital transformation and technological advancements; hence, better security measures and observability practices are essential. These attacks can breach your data or cause operational disruptions and financial loss.
By using SecOps observability, organizations can detect and respond to real-time threats. This thoughtful approach ensures that security logs, metrics, and incident data are seamlessly incorporated into monitoring solutions that generate insightful reports on attack patterns and vulnerabilities.
Further, compliance monitoring and auditing have become essential components of observability. They help organizations adhere to regulatory requirements by continuously tracking security configurations and behavior to prevent breaches. Thus, these open-source observability tools guarantee information security and real-time threat detection.
3. User Experience Observability (UXO)
Today, end-user performance and satisfaction have become a top priority. Organizations are shifting their focus to user experience observation (UXO) to achieve this result. This trend involves accurate user monitoring (RUM), which captures live user interactions to assess website and application responsiveness, and synthetic monitoring, simulating user actions to proactively detect potential issues.
Further, correlating UX data with infrastructure metrics allows organizations to view better how or what issues could affect user experience and accordingly make improvements that will eventually enhance customer satisfaction and engagement.
4. Full-Stack Observability Evolution
In 2025, full-stack observability is expected to grow and expand beyond traditional backend monitoring to encompass frontend applications, edge devices, and cloud-native environments. This approach ensures that every layer of your system and application is monitored, providing a unified view of your performance, behavior, and health.
Emerging technologies like eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filter) are crucial in advanced telemetry by offering high-performance, low-overhead data collection at the kernel level. Additionally, contextual data enrichment improves observability by correlating logs, metrics, and traces with relevant metadata, enabling deeper insights and faster issue resolution.
5. OpenTelemetry and Standardization
The adoption of OpenTelemetry is growing as organizations seek a standardized approach to data collection across diverse observability tools. OpenTelemetry is an open-source project that provides a unified framework for gathering logs, metrics, and traces, reducing vendor lock-in, and ensuring interoperability between monitoring solutions.
This practice supports various programming languages and cloud environments, allowing businesses to implement observability across microservices, containerized applications, and hybrid cloud architectures with minimal friction. The push for better communication in this movement is also expanding.
Beyond interoperability, OpenTelemetry is also driving innovation through its active open-source community. Developers, enterprises, and monitoring vendors collaborate to enhance its capabilities continuously, introducing new instrumentation techniques and improving data collection efficiency.
6. The rise of cost optimization within observability platforms
With the increasing complexity of IT environments, organizations focus on cost optimization within observability platforms. Many organizations are looking for ways to manage resource usage and control storage to manage observability costs effectively.
Sampling, data aggregation, and tiered storage are a few practices organizations adopt to minimize expenses without losing crucial insights. By optimizing observability spending, businesses can ensure they derive maximum value from their monitoring investments without unnecessary financial overhead.
Implementing Future Observability Practices
To successfully adopt the future of observability, an organization must implement the following best practices. By implementing these practices, organizations can handle the challenges of today’s complex systems and improve their digital experience.
1. Strategic Planning
Effective observability begins with a plan that clearly defines your goals aligning with business objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs). These goals should not only focus on performance optimization but also cover user experience. A strategic approach looks for essential metrics, such as slow response times, error rates, and system availability. Invest in the right tools and platforms, such as Motadata AIOps, to automate IT operations using AI and ML algorithms and gain detailed insight. You can also invest in their observability platform for long-term success.
Having clear goals and a mindset where observability is integrated into the development and operational workflows helps teams understand the value of real-time insights into system behavior. Thus, it ensures smarter resource use and cost optimization. Further, it enables faster issue detection and resolution using these open-source observability tools.
2. Data Management and Governance
The success of any observability project depends on how well you maintain data quality and consistency. Implementing strong data governance practices is essential for accurate data. Try collecting structured data and eliminating redundant or inaccurate information. Having high-quality data makes it easier to identify patterns and make informed decisions. Further, incorporate good data management practices, like cataloging and metadata management.
Organizations must define how long they will store logs, traces, and metrics to balance storage costs with the need for historical analysis. Proper data governance also involves addressing privacy and compliance requirements. Organizations must adhere to regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific guidelines to ensure that sensitive information is protected and that data collection practices are ethical and legally compliant.
3. Skills and Training
Observability solutions rely on advanced technologies, thus making it essential for IT professionals and engineers to develop expertise in AI/ML, data analytics, and cloud technologies. Knowledge of AI and machine learning practices will help enhance observability by automating anomaly detection and predicting potential failures. Data analytics further helps IT staff generate actionable insights from vast amounts of telemetry data. Organizations adopting cloud-native architectures must invest in and familiarize themselves with cloud observability tools for quality results.
Training employees is another crucial step for business continuity and smooth operations. Try running workshops or webinars to update your employees on the key observability trends and monitoring practices. The more your employees know how to use advanced observability tools, the better they can extract insights and make informed decisions.
Apart from improving your skills and training employees in key areas such as security integration, data visualization, AI-powered observability, etc., it is important to ensure proper collaboration among development, operations, and security teams. Proper cooperation and continuous learning can help close skill gaps and make it easier to manage modern systems.
Conclusion
Observability trends for 2025 are going to be game changers. Observability is constantly evolving, and you can expect some exciting advancements in AI-powered observability and other areas that will reshape the way IT teams monitor and optimize system performance. Some key observability trends for 2025 include AI-driven observability, increased adoption of OpenTelemetry, enhanced SecOps observability, and the shift toward full-stack visibility.
These advancements are expected to impact IT operations. They will improve incident detection, reduce downtime, and enable proactive decision-making. Organizations that embrace modern observability practices will gain a competitive edge by ensuring seamless digital experiences and operational resilience.
While the future of observability looks promising, businesses must prepare for potential challenges that will accompany these trends. So, invest in upskilling your teams, training them, and optimizing toolsets for maximum efficiency. Incorporate the above-listed best practices to prepare for the evolving landscape of observability. Further, invest in one of the best observability solutions for quality results and business continuity.
FAQs:
Monitoring involves collecting predefined metrics and logs to understand each system’s workings and identify issues. Conversely, Observability provides deeper insights into system health and behavior by analyzing telemetry data (logs, metrics, and traces) and proactively resolving issues.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) incorporation will allow organizations to automatically detect anomalies, predict potential problems by analyzing historical data, and reduce noise in alerting systems. Further, investing in AI-driven observability tools will help IT teams focus on critical issues and improve incident resolution time.
SecOps observability focuses on integrating security insights into observability frameworks. This practice allows team members to monitor system behavior and security. By implementing it, you can identify threats early, streamline compliance monitoring, and help teams quickly identify and mitigate security risks. With cyber threats on the rise, SecOps observability is essential for ensuring a secure IT environment.
OpenTelemetry is an open-source observability framework that standardizes data collection across applications. Its adoption in 2025 will drive interoperability, reduce vendor lock-in, and enable organizations to gain consistent insights across different platforms.
The three key pillars of observability are logs (a record of events), metrics (quantitative data on system performance), and traces (tracks request flow across distributed systems). Together, these three pillars provide a holistic view of system health and performance, helping organizations manage incidents in real time and make informed decisions.