In this modern digital age, implementing Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) practice has become crucial for businesses that demand for operational excellence and want to deliver a seamless customer experience.
Today, more than 90% of businesses rely on technology for achieving goals but what if they are unable to manage and deliver quality IT services to their customers? To ensure the unhindered and seamless functioning of technology, ITSM came into practice.
What is ITSM?
ITSM is a process that allows the IT department to oversee the comprehensive provision of information technology services to customers. This includes the planning, development, implementation, and maintenance of IT services.
The main objective of implementing this practice was to support organizational growth by coordinating IT services and processes with business goals.
It centers on integrating people, processes, and technology to generate value, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Let us explore more about ITSM – its workflows, importance, challenges, and ways to develop an ITSM strategy. Further, we will be highlighting how the traditional ITSM strategy and modern ITSM strategy differ.
Additionally, we will be covering some of the best practices that will help in successful implementation.
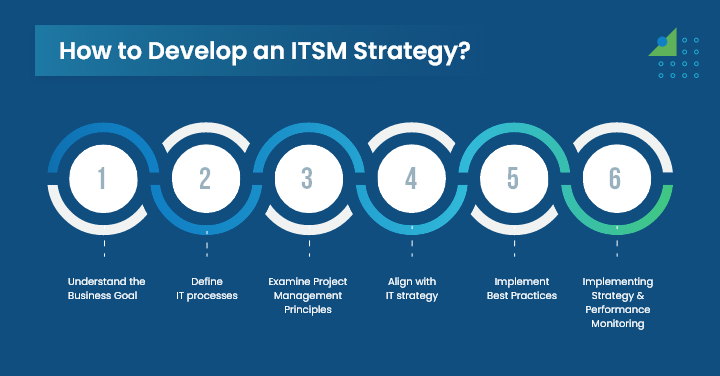
How to Develop an ITSM Strategy?
Organizations must create an effective ITSM strategy in order to match their IT services to their business goals and objectives.
When creating a strategy for your business, keep the following important steps in mind:
1. Understand the Business Goals:
It is essential to clearly define and understand the objectives and goals of a business. Assess the current IT infrastructure and ensure the IT services fulfill business demands and offer value by coordinating IT goals with business goals.
2. Define IT processes :
Determine and specify the IT processes needed to support the organizational objective such as change management, incident, problem, and service request management. Every process should have well-defined roles, responsibilities, and objectives.
3. Examine Project Management Principles :
An ITSM strategy’s creation and execution can benefit from the application of project management concepts. This involves establishing the goals of the project, setting deadlines for the plan, and allocating IT resources.
4. Align with IT strategy :
Make sure that the ITSM strategy aligns with the overall strategy that you have planned for your IT organization, i.e., resource requirements and related technologies essential for supporting IT services. It will help fill in the gaps or areas that require improvement in the existing IT infrastructure.
5. Implement Best Practices :
Another important thing to ensure is the adaptation of best practices for better efficiency and customer satisfaction. By implementing the right practices, you may place IT management procedures into effect.
6. Implementing Strategy and Performance Monitoring :
The last phase is putting the ITSM plan into action, which includes hiring staff, setting up the required technology, and creating the policies and procedures that will help the plan work. Also, keep an eye on the outcomes and modify the plan as necessary.
The Importance of ITSM in Enterprise
By implementing this practice, organizations can improve their efficiency level as well as production.
Further, it fosters collaboration between team members and minimizes downtime.
Let’s explore a few more reasons why implementing ITSM in an enterprise is important.
1. Reduces the Possibility of Digital Disruption
Even a minor change can be risky, particularly if it is poorly planned, assessed, or communicated to the IT team and the organization.
However, the probability of significant service or business disruptions is significantly reduced with ITSM. Effective communication with clients and other stakeholders is facilitated by formalized policies, processes, and roles.
2. Improved Accountability and Visibility
ITSM offers insights and transparency that help IT managers monitor event logs and resolve service requests in real time.
With its help, IT managers can review event logs to make sure services are provided consistently and in accordance with the policies and guidelines of the business.
They might also keep an eye on business activity taking place on the company network and spot policy violations.
3. Cost Management While Scaling
IT professionals must initiate hiring more personnel as businesses grow in size and complexity in order to avoid becoming overworked on tactical and operational tasks.
Thanks to automation techniques that reduce IT operators’ manual intervention, IT service management may help the scalability of IT operations without requiring more staffing.
4. Traditional vs Modern ITSM
ITSM has been around for a long time but there are a few modifications that have been made to keep up with the new digital realities.
Basically, there are two distinct methods for managing IT services inside an organization: Modern ITSM and Traditional ITSM.
Here are a few points on which they differ:
5. Approach
The traditional ITSM approach supports the structured and hierarchical model whereas the modern system comes with a more agile and flexible approach.
Also, the traditional method depends on manual processes and is less flexible. However, the modern approach supports automation, self-service, and more features.
6. User Experience
The modern method gives the user experience more weight. It strives to give end consumers options that are self-serve, easy to use, and intuitive.
On the other hand, the traditional method might place less emphasis on the end user experience and more emphasis on internal procedures and efficiency.
7. Technology Integration
Modern methods support automation, artificial intelligence, and more technologies that aid businesses in improving service delivery, problem management, and knowledge management.
With the help of these features, businesses can increase their productivity level, speed up and improve the accuracy of services, and automate repetitive processes.
However, the traditional approach relies more on human interaction and manual procedures.
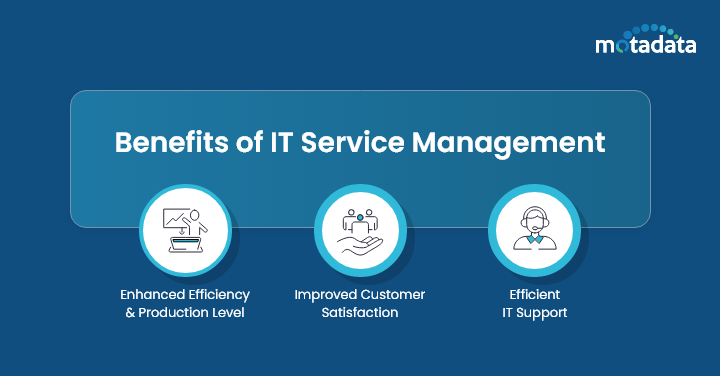
Benefits of IT Service Management
Right from improving efficiency level to delivering seamless customer experience, IT Service Management offers a wide range of benefits to an organization.
Here are some of the key benefits of IT Service Management:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Production Level
With the help of ITSM tools, businesses can automate and optimize the service delivery procedures resulting in enhanced efficiency.
Less manual effort and more automated tasks will further reduce downtime, lead to quick response time, and improve productivity levels.
2. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Delivering top-notch IT services that satisfy customer needs is the main goal of these ITIL processes. Organizations can increase customer satisfaction by using ITSM principles and offering user-friendly services.
3. Efficient IT Support
Effective IT support procedures, such as incident, problem, and service request management, can be established by enterprises with the use of ITSM.
These procedures guarantee that IT problems are quickly resolved and minimize delays to business activities.
Increased productivity, decreased downtime, and enhanced satisfaction with IT services are all results of effective IT assistance.
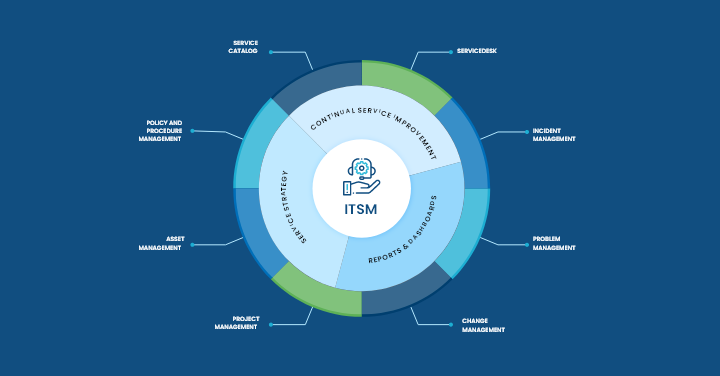
IT Service Management Workflows
Most people tend to confuse ITSM with basic IT support as it deals with IT on a regular basis.
However, it is a bit different as it involves a wide range of services, such as risk management, configuration management, change management, and end-to-end IT service delivery.
Let’s explore the different stages of ITSM processes and workflows.
1. Incident Management
Incident management is a process used by IT managers to address and resolve any type of service interruption.
When the affected service is returned to its regular operating state and can resume providing full service, the incident is deemed resolved.
Additionally, it entails clear communication with all concerned parties, cooperation across functional boundaries, elimination of obstacles that impede settlement, and ongoing enhancement of the incident management procedure.
2. Change Management
Managing changes in the systems, technology, and procedures that a business uses is known as change management.
Its objective is to minimize service disruption brought on by modifications and to lessen their impact on services.
3. Problem Management
The process of determining and controlling the reasons behind incidents is referred to as problem management.
It deals with locating the root causes of IT incidents and figuring out how to get rid of them to stop them from happening again.
4. Service Request Management
A formal request by users for something other than the resolution of an incident is called a service request. For example, software upgrades, printer access, and password resets.
By leveraging service request data, service request management assists firms in defining customer expectations and providing faster, more effective service.
Enabling consumers with knowledge and automating repetitive procedures significantly enhances the request resolution workflow.
5. IT Asset Management
The process of monitoring and controlling IT assets to guarantee their effective use is known as IT asset management.
Extending the life of assets, maximizing the number of assets in use, and strategically timing technological upgrades are all ultimate goals of IT asset management, which helps businesses cut expenses.
6. Knowledge Management
The process of producing, selecting, disseminating, and utilizing helpful information within the company is referred to as knowledge management.
Its objective is to guarantee that all stakeholders receive pertinent corporate policies and information in a timely manner, appropriate to their access levels.
Utilizing the knowledge already present in the business guarantees the existence of a single source of information, i.e., easily available.
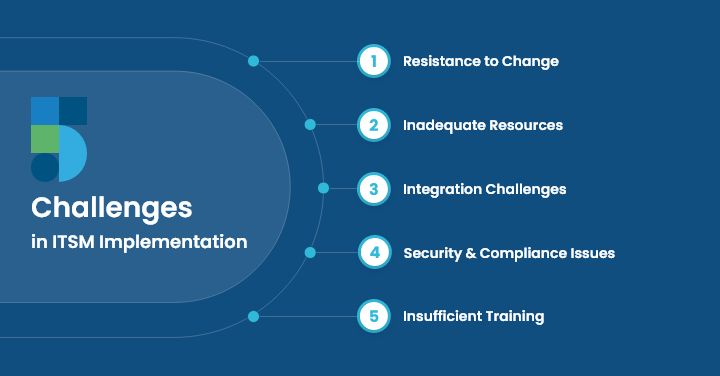
Challenges in ITSM Implementation
No doubt, there are several advantages to IT Service Management, but it also comes with a few challenges, including:
1. Resistance to Change
Significant adjustments to current organizational roles, responsibilities, and processes are frequently necessary for the implementation of ITSM.
Progress may be hampered by employees’ resistance to these changes if they are used to working in a particular manner.
2. Inadequate Resources
For ITSM adoption to be successful, there must be enough funding, experienced staff, and time.
Companies could underestimate the amount of resources needed or run into problems repurposing already-existing resources to help the endeavor.
3. Integration Challenges
Complex IT infrastructures with a wide range of applications and infrastructure can pose significant challenges when integrating ITSM tools and platforms with current systems and technology.
When integrating systems, there may be compatibility problems, data migration difficulties, and interoperability issues.
4. Security and Compliance Issues
When implementing ITSM, it is crucial to guarantee security and adherence to legal standards, particularly when handling sensitive data and important systems.
Organizations that neglect security and compliance issues run the danger of data breaches and legal liabilities.
5. Insufficient Training
Sufficient training and awareness-building initiatives are necessary to guarantee that staff members comprehend the goals of ITSM, how it affects their responsibilities, and how to utilize ITSM instruments and procedures efficiently.
Resistance might result from inadequate training, which can impede adoption.
ITSM Best Practices
The efficient management of IT services requires adherence to ITSM best practices.
The ITIL process enables businesses to guarantee the effectiveness and security of their IT services, systems, and procedures.
Here are a few best practices to implement:
1. Define Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
To ensure that IT services are delivered on time, SLAs are required. They should offer detailed information about service availability, resolution and response times.
A written and signed Service Level Agreement (SLA) should be established, containing quantifiable service level targets for performance, availability, response times, resolution times, and other quality parameters.
2. Automation
With automation, IT staff can save time and indulge in more complex projects. Additionally, this practice reduces human error and aids with compliance.
Automated workflows can simplify procedures and facilitate task management. Organizations can manage tasks related to asset management, change, and issue resolution through automation.
3. Create Procedures for Change Management
To lower the risk of unforeseen outages or service disruptions, organizations should implement change management procedures to ensure that they carefully plan and manage modifications to IT systems and services.
4. Monitor Performance
Performance monitoring is highly essential to ensure that each IT service operates as per the plan and that any issue found is fixed right away.
It involves monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to determine how effective IT services are.
This whole process keeping track of all types of data including the response time, availability, system usage, and other metrics.
5. Make a Plan for Risk Management
As a crucial component of service management, organizations should utilize risk management to recognize possible threats to IT systems and services and create plans to counter them.
Proactive actions should be taken as part of the plan to reduce possible risks and optimize the advantages of IT services.
It should also include a strategy for handling interruptions and getting back up quickly.
Conclusion
With digital transformation, modern corporate operations rely heavily on IT service management (ITSM), which helps companies achieve operational efficiency, spur innovation, and provide superior IT services.
Businesses can improve customer satisfaction level, maximize resource utilization, and gain a competitive edge in the current digital economy by adopting a strategic approach to ITSM.
Even if implementing ITSM can present difficulties, following best practices and committing to continuous development can guarantee long-term success and the realization of business value.
ITSM best practices are necessary for the efficient and successful delivery of IT services. Adopting the ITIL framework will enable IT services to be in line with business objectives and goals.
Meeting business needs and improving user experience require ongoing service improvement.
Service efficiency is attained by the application of best practices like incident and change management.
Best practices for IT service management are essential to both the performance of businesses as a whole and the digital transformation.
No doubt, this practice comes with various benefits like improved efficiency and productivity level, but at the same time there are a few challenges a business must keep in mind.
Above we have listed some of the top challenges of implementing ITSM strategy.
You can also rely on some of the top ITSM software like Motadata to streamline business processes.
The Intelligent Service Management tool uses AI-driven ticket assignment to help your IT service desk specialists perform more efficiently.
You can even try its free version and look out for its exclusive features.
FAQs
Incident Management, Change Management, Problem Management, Configuration Management, and Release Management are the five modules that make up ITSM. An area of service management, like handling modifications to IT systems or incident resolution, is the emphasis of each module.
Businesses can gain a lot of advantages from using ITSM principles. It enhances operational effectiveness and efficiency, which lowers costs and boosts productivity, and it helps match IT services with overall business goals. Better service delivery, quicker problem solving, and assistance in preserving regulatory and industry standard compliance are all further benefits of ITSM.
ITIL, COBIT, and ISO/IEC 20000 are the three most popular ITSM frameworks; each has a distinct focus and methodology. Whereas COBIT is more concerned with governance and risk management, ITIL places more emphasis on service lifecycle support. The ISO/IEC 20000 standard, on the other hand, offers a benchmark for the performance of IT services. You may determine which framework is best depending on your organizational unique demands and goals.