What is an SLA?
It’s an agreement between a customer and one or more service providers. The agreement can be legally binding or informally structured.
Parties involved in such agreements can be separate organizations or between teams within the same organization.
One common thing of every SLA is that the service to be provided is agreed upon and generally set by the customer.
For example, consider yourself to be a new joiner in your organization, and your HR initiates a ticket so the IT team can provide the credentials and the hardware for the employees to work. An SLA, in this case, will define the following:
- Resolution time: How long will it take for an IT technician to resolve such a ticket?
- Response time: How long will it take for technicians to respond to such tickets?
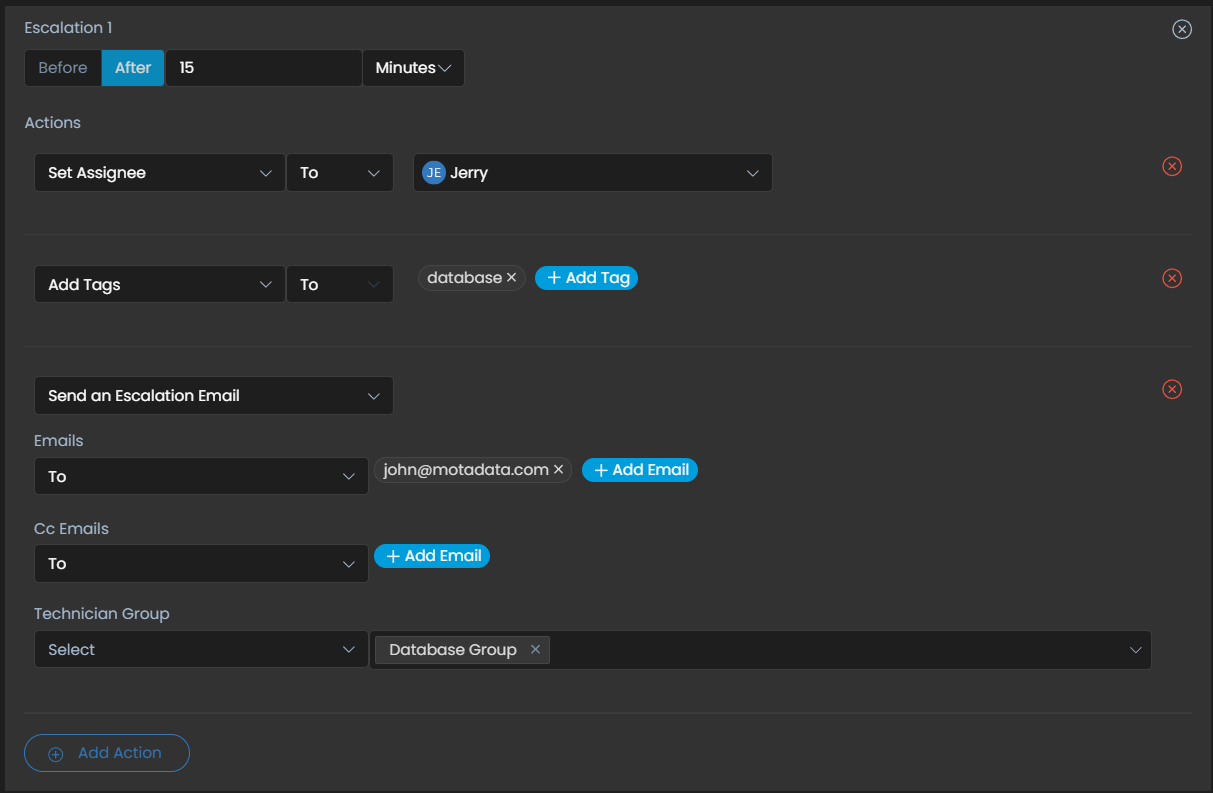
- Escalation rules: What actions will happen in the following events?
1. When response time is violated
2. When resolution time is violated
Motadata ServiceOps ITSM allows you to easily create SLAs with conditions, time criteria, and escalation rules.
Why is it Important to have SLAs?
Forming contracts is a standard practice in businesses, and having SLAs is no different; SLAs are important for the following reasons:
- SLAs give a sense of assurance to customers that their issues will be resolved timely.
- SLAs provide convenience because an SLA is a single document containing all the agreed-upon terms.
- It’s much more difficult to play the ignorance card when all the terms are clearly laid down.
Common mistakes when drafting SLAs
Service providers should offer a clear proposal and a warranty for their services, and that should be the priority. Creating a Service Level Agreement (SLA) is the only way to protect themself and their customers and ensure the relationship is successful. But, for doing that they must avoid making a few mistakes.
1. Not having a clear and specific scope of SLA agreement
Many service providers claim the availability of 99.95%, but that number varies on certain restrictions and conditions. It is essential to mention the clear and specific scope of SLA when creating an agreement.
2. Create too many SLAs
Defining too many SLAs may contradict each other, and it may get complicated for service providers to know which tasks are important to focus on and that need to be actively managed.
3. Unrealistic performance targets
Unrealistic expectations from both parties can create conflict in a successful SLA, so it is important to agree on measurable service requirements to have constant services.
4. SLA as a conflict resolution
Sometimes service providers and clients just rely on SLA during conflicts, which is not the solution, and it is kind of a mistake that may impact negatively the parties.
5. Not agreeing on SLAs
When it comes to creating and implementing effective SLA, negotiations, clarifications and agreements are extremely important. In some cases, parties assume that the expectations are clear, but they are not.
What to Include in Your SLA?
The SLA should include the following:
- Statement of objectives
- Scope of services to be covered
- Service provider responsibilities
- Customer responsibilities
- Performance metrics (response time, resolution time, etc.)
- Penalties for contract breach/exclusions
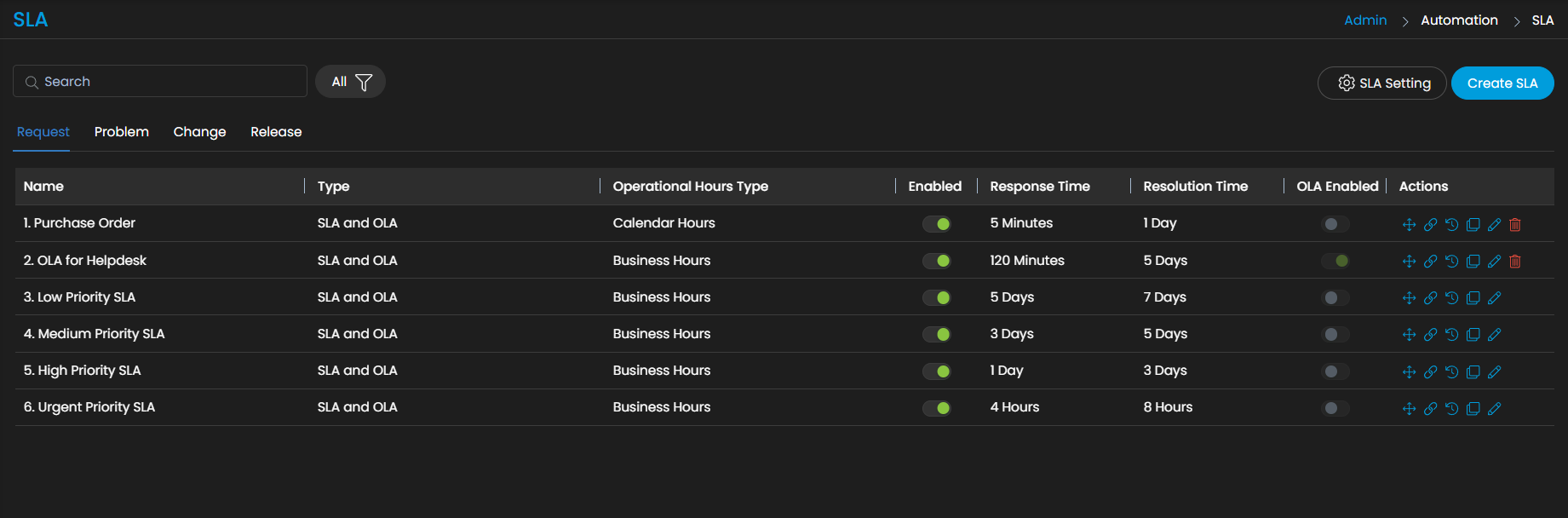
How to Set SLA in ServiceOps?
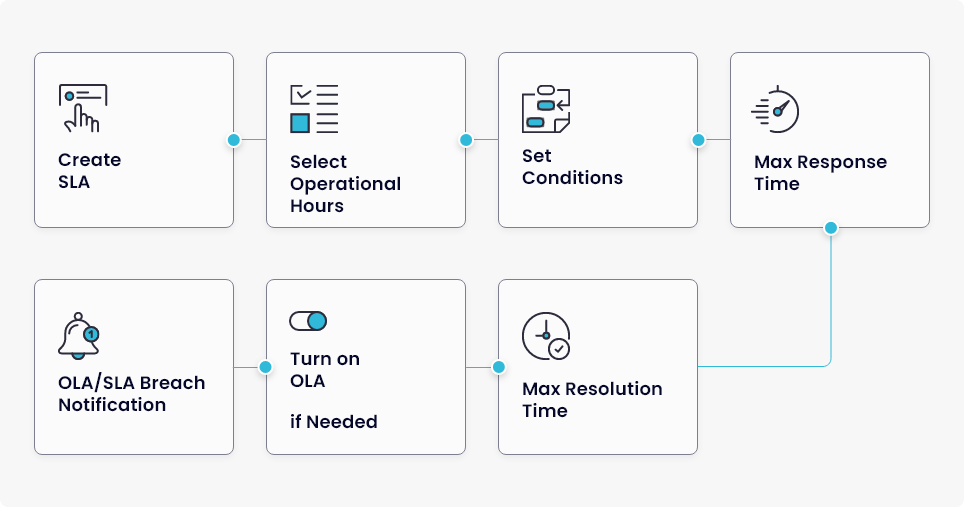
Creating SLA
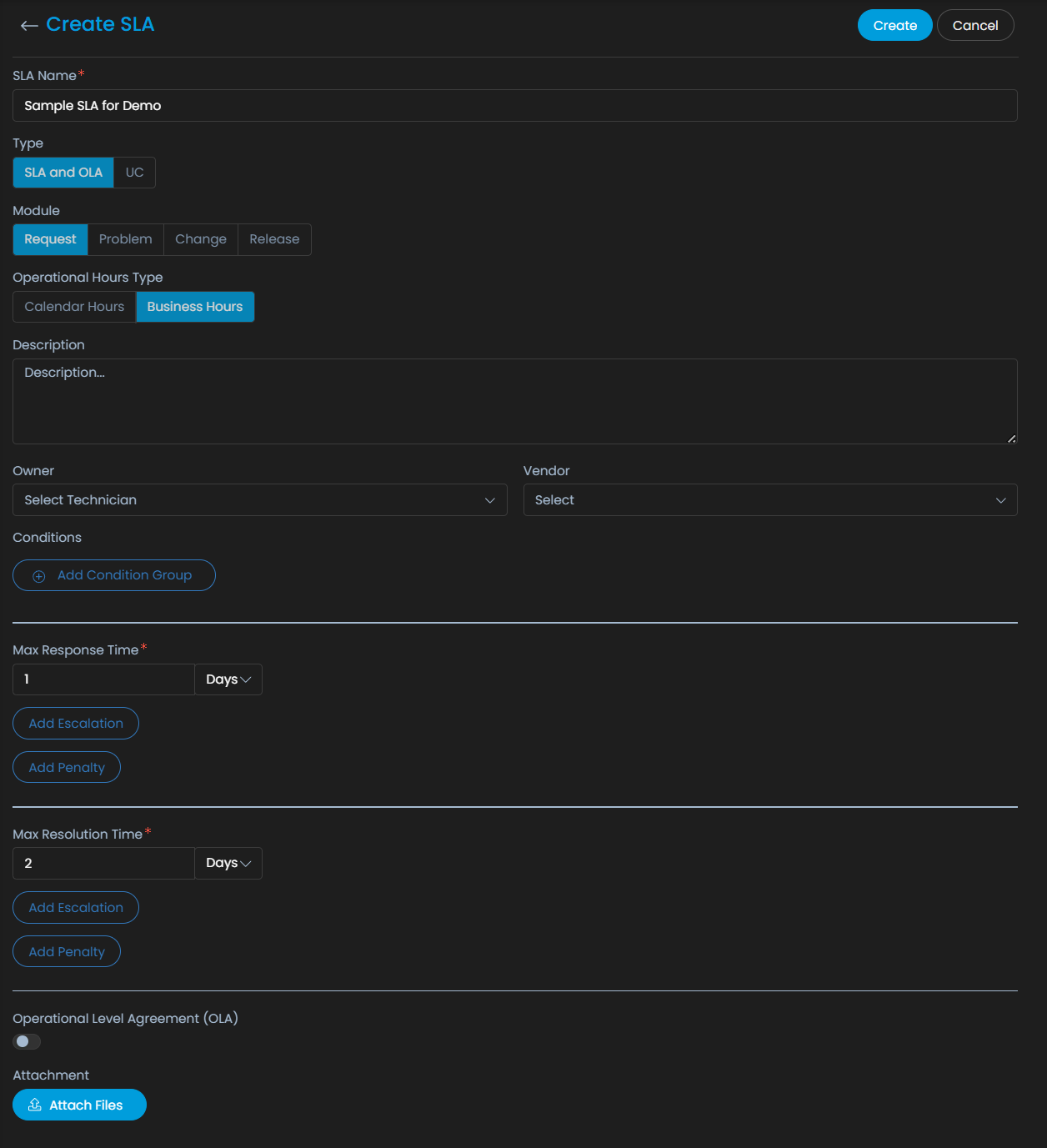
ServiceOps allow you to create SLAs by just following some simple steps.
Select Operational Hour Support
The SLA in ServiceOps allows you select business hour support during calendar hours or business hours.
- Calendar Hours: The SLA takes 24×7 as the working hours.
- Business Hours: The SLA uses the settings from the business hours section.
Features for SLA
Service level agreement – Motadata SLAs indicate the urgency level, response time, time taken to resolve tickets, and they also determine the escalation rules when tickets do not get resolved within a predefined time frame.
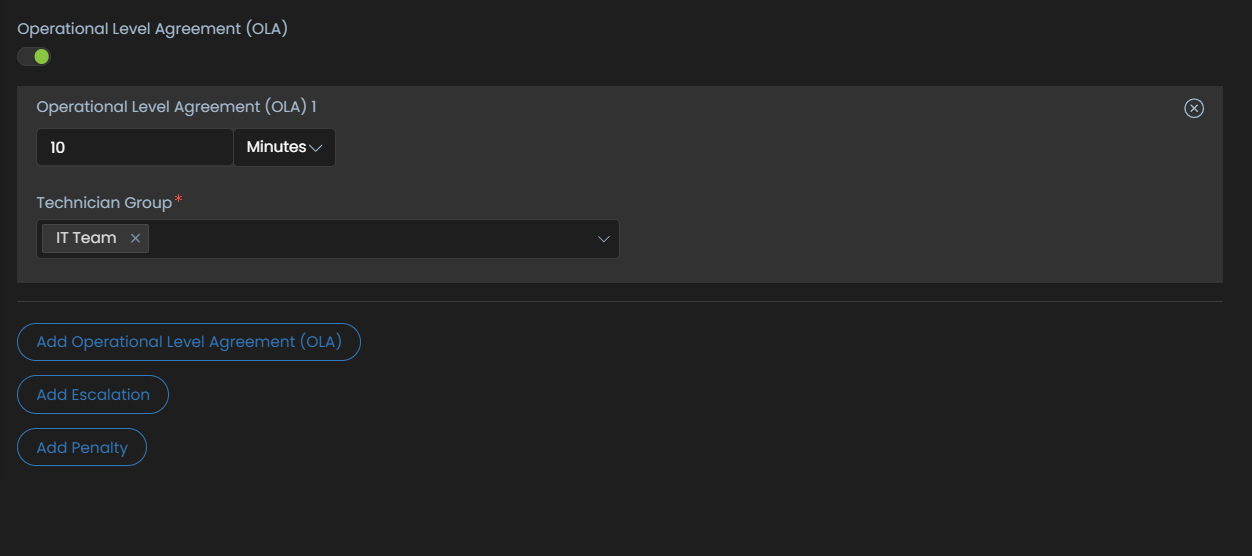
Operational level agreement – OLAs are contracts that take place between internal teams to fulfil the SLA. OLAs are usually like SLAs but include service targets.
Underpinning contract – The Underpinning Contracts (UC) are contracts between the IT Service Providers and the external vendors.
Penalty – Whenever an SLA is breached, you can select the type of penalty that you want to apply. There are two kinds of penalties – fixed penalty and cumulative penalty.
Escalation – When one does not get a response in the defined time frame of SLA, the escalation rule gets applied.
Setting OLA
Once the operational hours and conditions are defined, the next step is to decide the OLA if needed. Here are the steps to define Operational Level Agreements.
SLA Breach Notification (Avoiding SLA breaches)
The SLA breach notifications allow you to select a pre-defined template fetched from the event notification section for all types of automatic notifications sent by the system in case of an SLA Breach.