I want to start this blog with a hard fact!
The perception of a brand can change from a single bad experience.
Think of a time when you decided to change your brand loyalty just because the brand couldn’t give service on time.
Service delivery on time is so critical that service delayed is the same as service denied.
The service desk is an important part of any organization that is responsible for service delivery; failure of which could directly impact the image of the company, doesn’t matter whether the service desk is for internal or external customers.
IT leaders use Service Level Agreements (SLAs) as a powerful tool to ensure they resolve incoming issues on time, ensuring timely service delivery.
Before I continue with this blog, here’s a short overview of what I am going to cover:
- What is an SLA?
- Why is it important to have SLAs?
- 3 common types of SLA
- What is Service Level Management?
- What are the main components to define a good SLA?
- How to set SLA metrics?
- What are some common SLA metrics?
What is an SLA?
It’s an agreement between a customer and one or more service providers. The agreement can be legally binding or informally structured.
Parties involved in such agreements can be separate organizations, or it can be between teams within the same organization.
One common thing of every SLA is that the service to be provided is agreed upon and generally set by the customer.
For example; consider yourself to be a new joiner in your organization, and your HR initiates a ticket so the IT team can onboard you.
An SLA in this case will define the following:
- Resolution time: How long will it take for a technician to resolve such a ticket?
- Response time: How long will it take for technicians to respond to such tickets?
- Escalation Rules: What actions will happen in the following events:
1. When response time is violated
2. When resolution time is violated
Motadata ServiceOps ITSM allows you to easily create SLAs with conditions, time criteria, and escalation rules.
Why is it Important to have SLAs?
Having an SLA [service level agreement] is just as important as having the HRMS Software, because without it your whole management system will start to crumble around!
Forming Software Development contracts is a standard practice in businesses, and having SLAs is no different; SLAs are important for the following reasons:
- SLAs give a sense of assurance to customers that their issues will be resolved timely.
- SLAs provide convenience because an SLA is a single document containing all the agreed-upon terms.
- It’s much more difficult to play the ignorance card when all the terms are clearly laid down.
Undoubtedly, SLAs are vital instruments, and so is their effective management. Risking your SLAs with traditional contract management approaches may lead to agreement non-compliance. On the other hand, using an AI-based contract management software helps automate critical tasks and obligation management—ensuring compliance with SLAs at all times.
3 Common Types of SLAs
There are three types of SLAs used in businesses, they are:
1. Customer-based SLA:
It’s a kind of agreement done with a single customer containing all the relevant services required by the customer.
Generally, such agreements leverage a single contract, which is convenient for the vendor because of the simplicity.
For example; a VoIP service provider may club all related voice services into a single contract.
2. Service-based SLA:
It’s a contract defining one service for all customers. The SLA depends on unchanging standards, which makes it simple and straightforward for vendors.
For example, an SLA governing how the helpdesk resolve tickets will be valid for all customers who agree to receive its service.
3. Multi-level SLA:
In such an agreement, the end-user has the option of customization according to his/her needs; the user can add several conditions to create a suitable service.
The organization divides the SLA into different levels, each addressing different customers within the same organization.
- Corporate Level: It is a comprehensive description of the agreement, covering generic SLM issues, suitable for everyone in the organization.
- Customer Level: Cover SLM issues relevant to a particular group of customers.
- Service Level: Covers SLM issues for a particular service relevant for a particular customer group.
Streamline your business process across the organization and drive digital transformation with Motadata’s unified ITSM platform (PINKVERIFY certified).
What is Service Level Management (SLM)?
Service Level Management (SLM) manages service level agreements by defining, documenting, evaluating, and assessing the level of services offered.
With good SLM practices, an organization can:
- Meet and exceed customer expectations
- Define basic criteria for gauging the status of offered services
- Determine practical conditions that it can handle
- Adhere to the terms and conditions agreed upon with customers.
- Prevent future disagreements and conflicts
What are the main components to define a good SLA?
A service level agreement outlines what two organizations want to accomplish with their contract.
It specifies each side’s obligations with expected results supported by performance metrics.
While SLAs focus on specific services, they’re often part of a broader Master Services Agreement (MSA).
Using AI for an MSA can help ensure comprehensive coverage of all necessary terms while maintaining consistency with individual SLAs.
SLAs usually define all agreed-upon services along with their time frames.
Information on protocols for tracking the service performance as well as procedures to solve problems are also covered in the contract.
Incorporating a service agreement template can help in clearly outlining these aspects, ensuring both parties have a mutual understanding and agreement.
How to set SLA metrics?
SLAs incorporate metrics that assess the efficiency of the service provider’s performance so it is important to choose metrics that are under the service provider’s control yet fair to both parties involved.
In SLAs, it is important to define a benchmark for the metrics.
You should establish this standard rationally at the start and adjust it as more data on the metrics becomes available.
Capturing accurate SLA metrics quickly and automatically further tightens the benchmark.
It is also preferable to have less precisely calculated metrics than a large number of metrics that no one would have time to analyze.
Get some practical tips for setting SLA Metrics – 5 Practical tips to set, measure and report SLAs
What are some common SLA metrics?
The idea behind SLA metrics is to measure the quality of work done by a service provider. An SLA can contain one or more mutually agreed-upon metrics to measure performance.
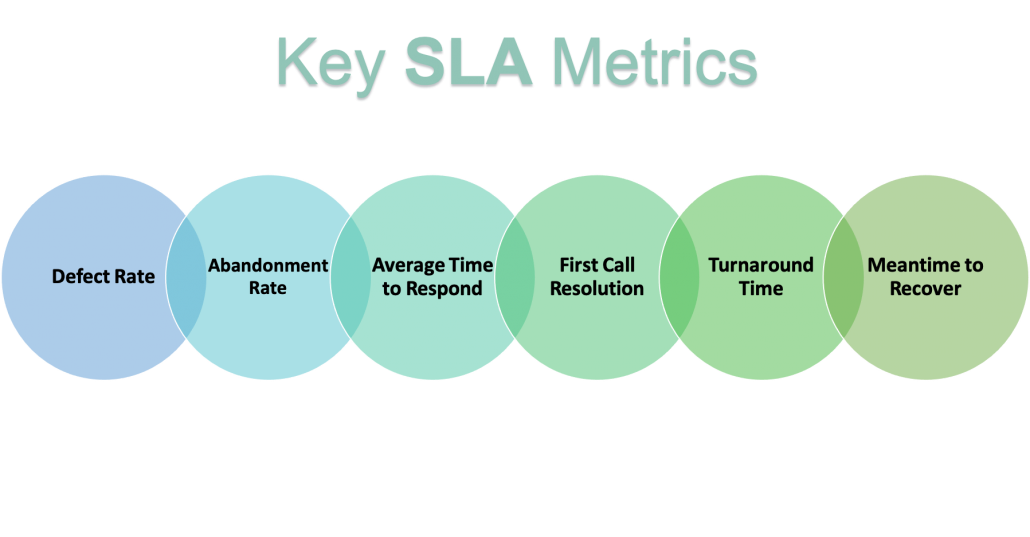
Here are some common metrics used with regards to a service desk:
- Defect rate: Percentage of errors done while delivering a solution.
- Abandonment rate: Percentage of tickets not responded to within the response time. Download Motadata ServiceOps ITSM and see how easy it is to set an SLA response time.
- Average time to respond: Average time it takes for a technician to respond to a ticket.
- First call resolution: Percentage of tickets resolved without the requester having to initiate a second contact.
- Turnaround time: The average time it takes to do a certain task.
- Meantime to recover: The average time it takes to resolve a certain kind of service outage.
Motadata ServiceOps ITSM allows its users to capture all key SLA metrics through its reporting module.
Conclusion
Creating SLAs is the first step in building a relationship between customers and service providers; they bring a sense of clarity as to what to expect from each party.
Each party can be held responsible to keep their end of the bargain. Sometimes, compromises may happen due to resource constraints; in such cases, the customer may have to change their requirement.
Capture all your SLA key metrics and measure the performance efficiently with Motadata’s unified ITSM tool that uses AI/ML to streamline the overall business operations – Click here to know more about our product.
FAQs:
An SLA is a formal agreement between a service provider and a customer, outlining the expected level of service, performance metrics, and responsibilities of both parties.
The main types are Customer-Based SLAs, Service-Based SLAs, and Multi-Level SLAs (including corporate, customer, and service levels).
Common metrics include uptime, response time, resolution time, throughput, and service availability.
SLAs are monitored through performance reports, dashboards, and automated monitoring tools to ensure compliance with agreed standards.